CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (10): 4327-4349.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200693
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tianyi LAI( ),Jikang WANG,Tian LI,Sha BAI,Xiaojie HAO,Yufei ZHAO(
),Jikang WANG,Tian LI,Sha BAI,Xiaojie HAO,Yufei ZHAO( ),Xue DUAN
),Xue DUAN
Received:2020-06-02
Revised:2020-07-17
Online:2020-10-05
Published:2020-10-05
Contact:
Yufei ZHAO
通讯作者:
赵宇飞
作者简介:来天艺 (1996—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Tianyi LAI,Jikang WANG,Tian LI,Sha BAI,Xiaojie HAO,Yufei ZHAO,Xue DUAN. Photoelectrochemical water splitting into active hydrogen/oxygen species coupling with hydrogenation/oxidation process using layered double hydroxides-based nanocatalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4327-4349.
来天艺,王纪康,李天,白莎,郝晓杰,赵宇飞,段雪. 光电解水产活性氢/氧耦合加氢/氧化过程用水滑石基纳米材料[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4327-4349.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.2 A polyhedral representation of the ZnTi-LDH structure (a); H2 evolution productivity of MTi-LDH (b); ESR spectra recorded for DMPO-·O2- in methanol dispersion (c)[29]; Proposed structural model of energy states for the Ti3+ self-doped NiTi-LDH and schematic illustration of the O2 evolution process over the NiTi-LDH nanosheet under visible-light irradiation (d); Fluorescence spectra (e); O2 evolution from aqueous solution using 10-2 mol·L-1 AgNO3 as the sacrificial acceptor under visible-light using NiTi-LDH with different thickness (f)[30]

Fig.3 Schematic illustration for the preparation of Cu2O@ZnCr-LDH hollow coreshell photocatalyst(a); Rate of gas generation as function of irradiation time (b); Schematic illustration for the photoexcited electron separation/transport in the Cu2O@ZnCr-LDH system (c)[33]; Gas generation rate (d); Schematic definition for S- and W-parameters in CDB-PAS measurements of Cu2O@ZnCr-LDH (e)[34]
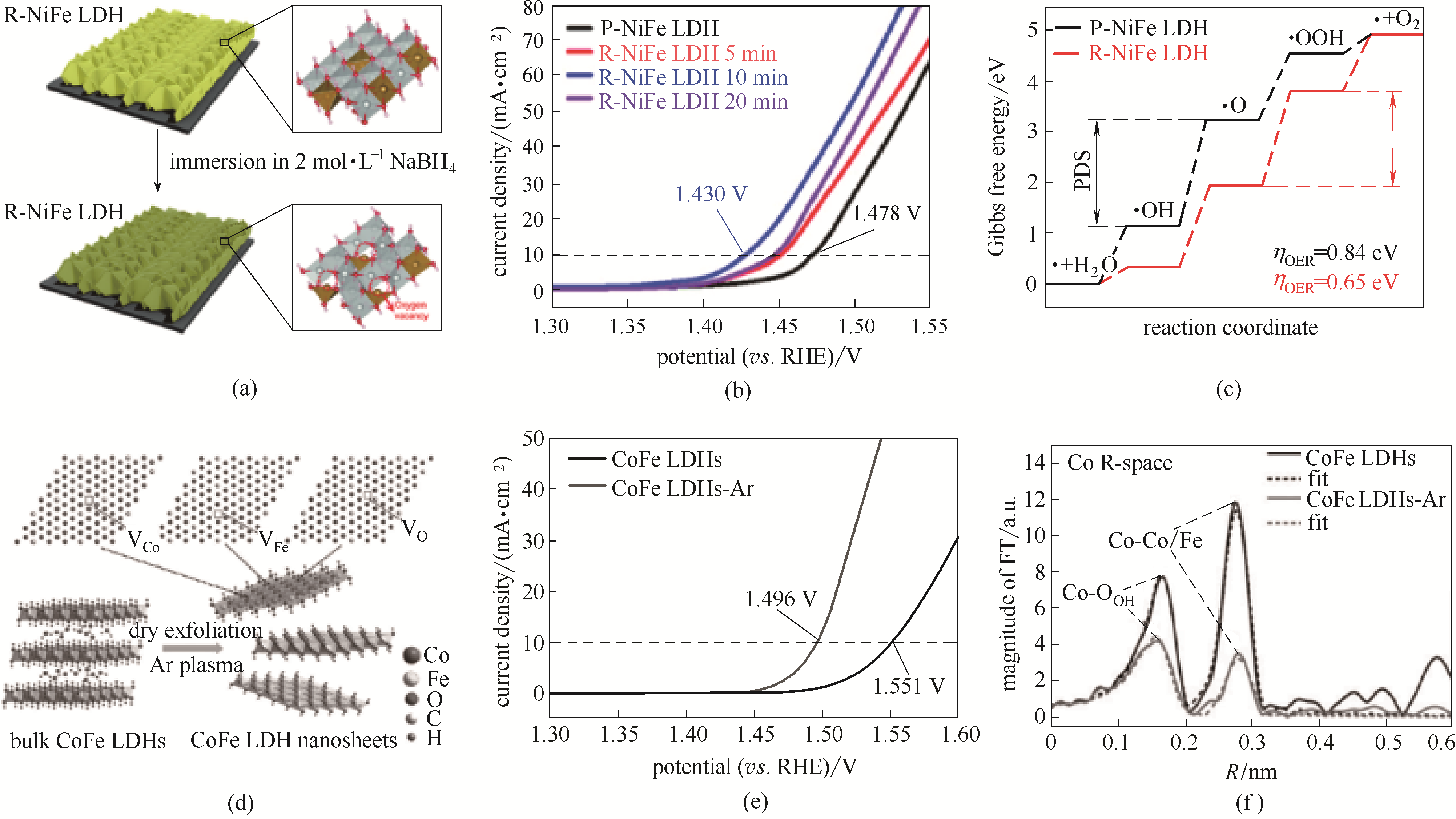
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of introducing oxygen vacancy defects to NiFe-LDH nanoarray electrode (a); Linear sweep voltammetry polarization curves of as-prepared NiFe-LDH after NaBH4 treatment (b); Free energy plots calculated results of OER process NiFe-LDHs treated by NaBH4 (c)[39]; CoFe-LDH nanosheets by Ar plasma exfoliation (d); LSV curves of bulk CoFe-LDHs and ultrathin CoFe-LDH nanosheets (e); Magnitude of the k3-weighted Fourier transforms of the Fe edge XANES spectra for bulk CoFe-LDH and ultrathin CoFe-LDH (f)[9]

Fig.5 Schematic illustration for the synthesis of CoNiP@NiFe-LDH hierarchical arrays (a); Photographs of water-splitting system (b); LSV results of two-electrode cell assembled by various materials (c)[44]; The *H Gibbs free energy of different catalysts (d)[48]

Fig.6 Schematic illustration for the fabrication of TiO2/ZnFe-LDH-PE NAs (a); J-V curves (b); Schematic illustration for the PEC water oxidation process over the TiO2/ZnFe-LDH photoanode (c)[50]; Schematic illustration of the fabrication of ZnO@ CoNi-LDH core-shell NWs array(d); IPCE for ZnO@LDH electrode with various LDH deposition time (e); Schematic illustration of the photoelectrochemical water oxidation process by the as-obtained ZnO@ CoNi-LDH core-shell NWs array (f)[53]

Fig.7 Scheme of energy levels and charge transfer pathways of C3N4 and MMO@C3N4(a); The light-driven H2O2 generation in O2-equilibrated conditions over MMO@C3N4, Ni@C3N4, Fe@C3N4, and MMO/C3N4-Mix (b)[60]; The light-driven H2O2 generation (c); H2O2 decomposition over TiO2-ZnTiO3, ZnTi-MMO and P25 (d)[61]

Fig.8 Alcohols STY at different pressures over catalysts with four Cu/Fe ratios (1/1, 2/1, 4/1, and 6/1)(a); CO-TPD profiles of Fe1, Cu4, and CuxFey samples (b)[69]; ESR spectrum over Ni-NiO structure (c)[70]; The potential energy profiles for CO2 formation, C2H4 adsorption, and hydrogenation under excited states on Fe3O4, 4O/Fe, and 4O/Fe3Zn (d); Fabrication of Co-x catalysts by H2 reduction of ZnCoAl-LDH nanosheets at 300—700℃ (e)[71]

Fig.9 Schematic illustration of the morphological evolution process of the as-obtained flower-like hierarchical LDH microspheres(a); N2-sorption isotherms and pore size distribution (inset) of MgFe-LDH microspheres with different inner architecture (b); Cyclic voltammograms at the MgFe-LDH microspheres modified electrodes (c)[76]; Design schematic of the Au-NCs/LDH catalyst (d)[77]; Time course for the dehydrogenation of benzyl alcohol over Au/HT catalyst prepared by the DP method (e)[78]

Fig.11 Selectivity of CH4, CO, and H2 in CO2PR on monolayer NiAl-LDH under different wavelength (a); Illustration for the species of defects on monolayer NiAl-LDH. VM represents metal defect (M=Ni, Al), VOH represents the hydroxyl defect (b); The energy levels for the singlet and triplet excited states of photosensitizer Ru(bpy)3Cl2, together with the band edge placements for the CBM, defect state, and valence band minimum (VBM) of monolayer NiAl-LDH (VNi&OH) versus the normal hydrogen electrode (NHE) (c)[86]; Illustration of sulfur vacancy-promoted selective synthesis of functionalized aminoarenes via transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes with H2O as the hydrogen source over a cobalt sulfide nanosheet cathode (d)[87]; Illustration of selective transfer semihydrogenation of alkynes with H2O (D2O) as the H (D) source over a Pd-P cathode (e)[88]
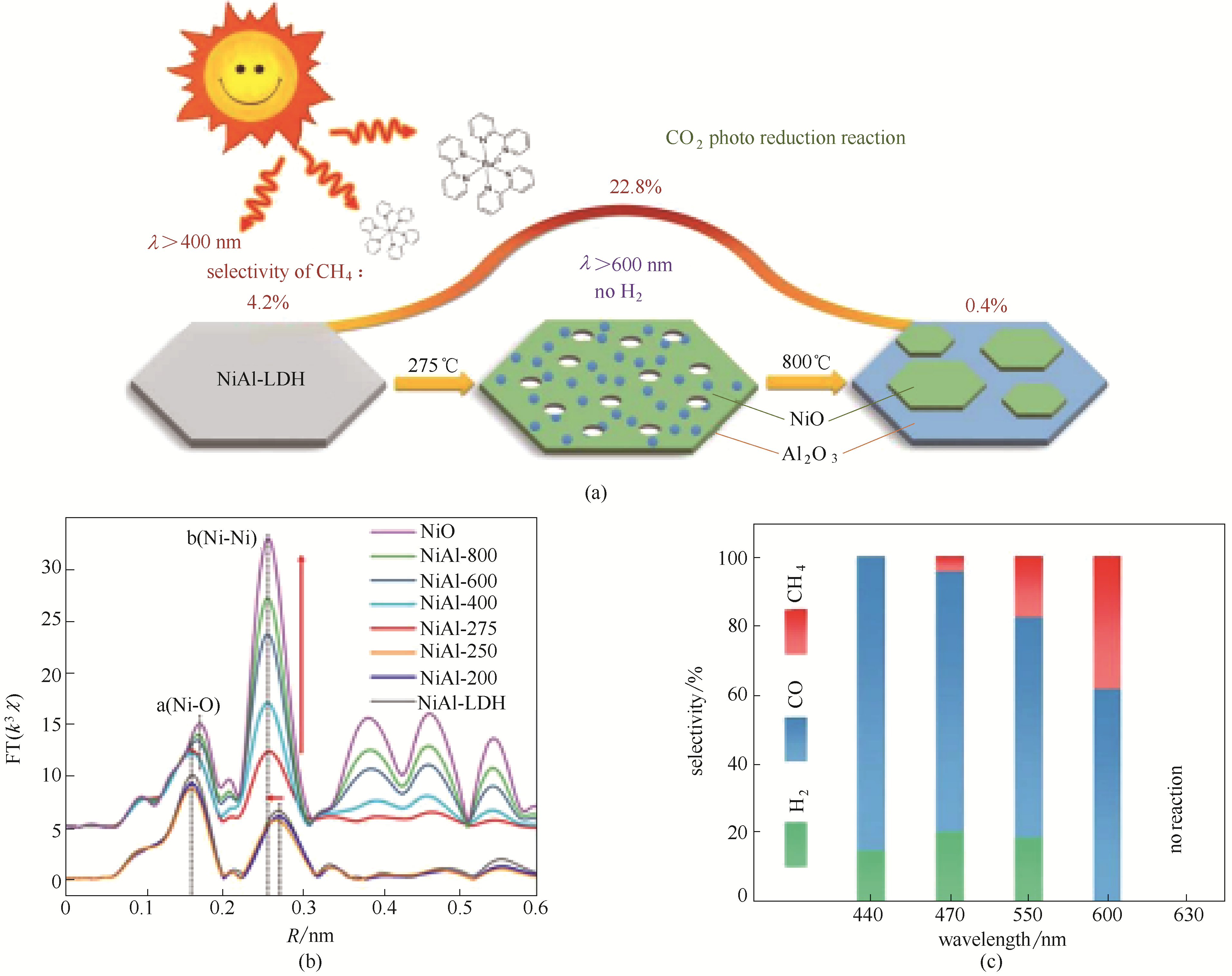
Fig.12 Schematic illustration of defect-containing NiO derived from the topological transformation of NiAl-LDH(a); The corresponding k3-weighted FT spectra of NiO, NiAl-x, and NiAl-LDH (b); Selectivity of NiAl-275 under different monochromatic light (c)[89]
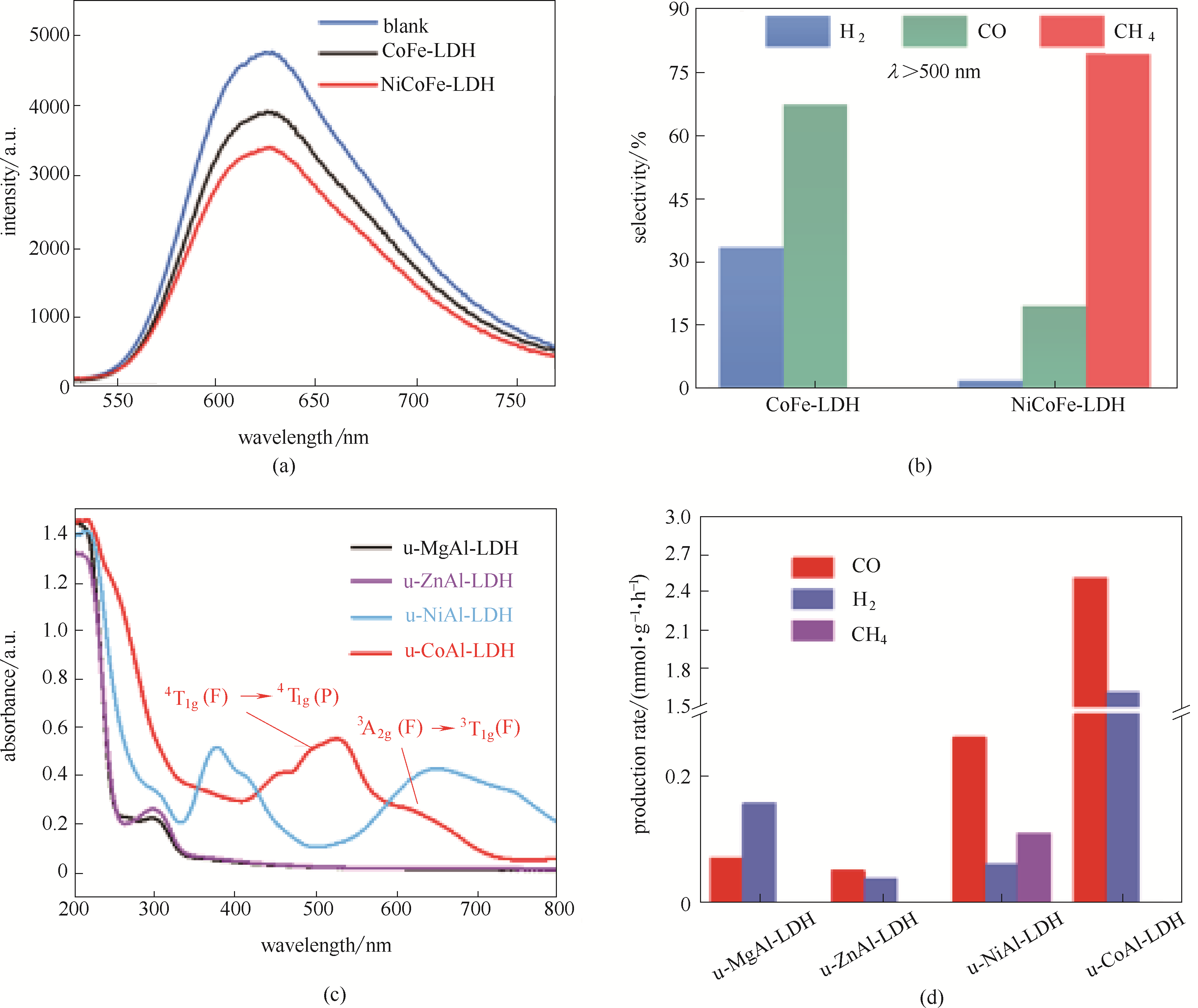
Fig.13 Room-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra of CoFe-LDH and NiCoFe-LDH (a); Selectivity of CH4, CO, and H2 under irradiation above 500 nm for CoFe-LDH and NiCoFe-LDH (b)[90]; UV-vis spectra for the various u-MAl-LDH photocatalysts (c); Production rates of CO, H2, and CH4 on various u-MAl-LDH photocatalysts in CO2PR under visible light (d)[91]

Fig.14 Schematic illustration of photocatalytic CO2 reduction to tunable syngas on CoAl-LDH/MoS2 heterostructures with different catalyst concentrations (a); LDH/MoS2 nanocomposite yield and selectivity of CO and H2 in CO2PR with different concentrations (b)[94]; Schematic diagram of the selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction by different anion intercalated NiAl-LDH (c)[95]; Selectivity of LDH and Ce-x (d)[96]
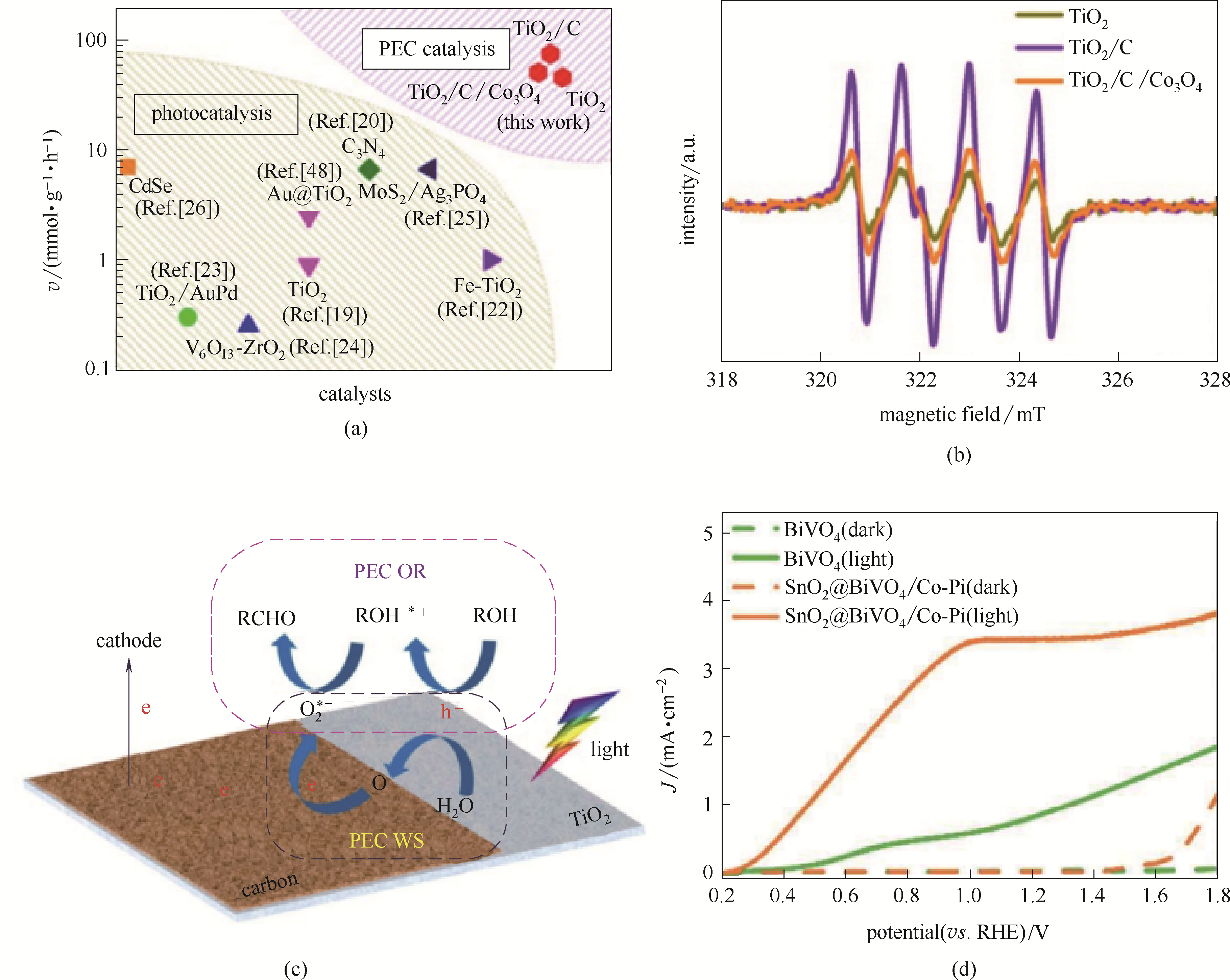
Fig.15 Comparison of reaction rate between PEC catalysis in this work and photocatalysis reported previously (the Ref. numbers in the figure were Ref. numbers of the Ref.[97])(a); DMPO spin-trapping ESR spectra recorded for DMPO-·O2- over TiO2, TiO2/C, and TiO2/C/Co3O4 sample, respectively (b); Schematic illustration for the PEC WS-OR coupling process (c)[97]; Photocurrent-potential curves under illumination of urea oxidation (d)[98]

Fig.16 Supercell model of ZnTi-LDH layer doped with VO vacancies(a); Schematic band diagrams (b); Reaction time profiles of phenol (c); Conversion of benzene oxidation (d); 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) as spin-trapping agent under UV-vis light irradiation to detect ·OH (e) and·O2- (f), respectively[99]

Fig.17 HMF oxidation process and products(a); Schematic diagram of the electrochemical system used for the overall cell reactions (b); Concentration changes of HMF and its oxidation products with the time of chronoamperometric tests (c); LSV curves of the NiFe-LDH nanosheet growth on carbon fiber paper (d)[102]
| 1 | Yao S, Zhang X, Zhou W, et al. Atomic-layered Au clusters on α-MoC as catalysts for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction [J]. Science, 2017, 357: 389-393. |
| 2 | Luo J, Im J H, Mayer M T, et al. Water photolysis at 12.3% efficiency via perovskite photovoltaics and earth-abundant catalysts [J]. Science, 2014, 345: 1593-1596. |
| 3 | Tang C, Cheng N, Pu Z, et al. NiSe nanowire film supported on nickel foam: an efficient and stable 3D bifunctional electrode for full water splitting [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(32): 9351-9355. |
| 4 | Wang J, Li Z, Li X, et al. Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from glycerol and water over nickel-hybrid cadmium sulfide quantum dots under visible-light irradiation [J]. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(5): 1468-1475. |
| 5 | Wang J, Cui W, Liu Q, et al. Recent progress in cobalt-based heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical water splitting [J]. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(2): 215-230. |
| 6 | Hou Y, Lohe M R, Zhang J, et al. Vertically oriented cobalt selenide/NiFe layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets supported on exfoliated graphene foil: an efficient 3D electrode for overall water splitting [J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(2): 478-483. |
| 7 | Liu P, Yang S, Zhang B, et al. Defect-rich ultrathin cobalt-iron layered double hydroxide for electrochemical overall water splitting [J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface, 2016, 8(50): 34474-33481. |
| 8 | Wang Y, Xie C, Zhang Z, et al. In situ exfoliated, N-doped, and edge-rich ultrathin layered double hydroxides nanosheets for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(4): 1870119. |
| 9 | Wang Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z, et al. Layered double hydroxide nanosheets with multiple vacancies obtained by dry exfoliation as highly efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysts [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(21): 5867-5871. |
| 10 | Li W, Jiang N, Hu B, et al. Electrolyzer design for flexible decoupled water splitting and organic upgrading with electron reservoirs [J]. Chem., 2018, 4(3): 637-649. |
| 11 | Hughes M D, Xu Y J, Jenkins P, et al. Tunable gold catalysts for selective hydrocarbon oxidation under mild conditions [J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7062): 1132-1135. |
| 12 | Fukuzumi S, Ohkubo K. Selective photocatalytic reactions with organic photocatalysts [J]. Chem. Sci., 2013, 4(2): 561-574. |
| 13 | Ide Y, Torii M, Sano T, et al. Layered silicate as an excellent partner of a TiO2 photocatalyst for efficient and selective green fine-chemical synthesis [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(32): 11784-11786. |
| 14 | Han G, Jin Y H, Burgess R A, et al. Visible-light-driven valorization of biomass intermediates integrated with H2 production catalyzed by ultrathin Ni/CdS nanosheets [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(44): 15584-11587. |
| 15 | Wang D, Wang M, Li Z, et al. Fe-based metal-organic frameworks for highly selective photocatalytic benzene hydroxylation to phenol [J]. ACS Catal., 2015, 5(11): 6852-6857. |
| 16 | Zheng J, Lyu Y, Qiao M, et al. Photoelectrochemical synthesis of ammonia on the aerophilic-hydrophilic heterostructure with 37.8% efficiency [J]. Chem., 2019, 5(3): 617-633. |
| 17 | Fan G, Li F, Evans D G, et al. Catalytic applications of layered double hydroxides: recent advances and perspectives [J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(20): 7040-7066. |
| 18 | 王瑞瑞,赵有璟,邵明飞, 等. 层状双金属氢氧化物用于催化水氧化的研究进展 [J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(1): 54-72. |
| Wang R R, Zhao Y J, Shao M F, et al. Recent progresses in water oxidation over layered double hydroxide catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(1): 54-72. | |
| 19 | Zhang F, Xiang X, Li F, et al. Layered double hydroxides as catalytic materials: recent development [J]. Catal. Surv. Asia, 2008, 12(4): 253-265. |
| 20 | Wang Q, O'Hare D. Recent advances in the synthesis and application of layered double hydroxides (LDH) nanosheets [J]. Chem. Rev., 2012, 112: 4124-4155. |
| 21 | Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Waterhouse G I N, et al. Layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for dinitrogen fixation [J]. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(42): 1703828. |
| 22 | Zhao Y, Waterhouse G I N, Chen G, et al. Two-dimensional-related catalytic materials for solar-driven conversion of COx into valuable chemical feedstocks [J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(7): 1972-2010. |
| 23 | Hong W T, Risch M, Stoerzinger K A, et al. Toward the rational design of non-precious transition metal oxides for oxygen electrocatalysis [J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(5): 1404-1427. |
| 24 | Gao R, Yan D. Recent development of Ni/Fe‐based micro/nanostructures toward photo/electrochemical water oxidation [J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(11): 1900954. |
| 25 | Ping J, Wang Y, Lu Q, et al. Self-assembly of single-layer CoAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets on 3D graphene network used as highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(35): 7640-7645. |
| 26 | Qiao B, Wang A, Yang X, et al. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx [J]. Nat. Chem., 2011, 3(8): 634-641. |
| 27 | Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode [J]. Nature, 1972, 238: 37-38. |
| 28 | Silva C G, Bouizi Y, Fornés V, et al. Layered double hydroxides as highly efficient photocatalysts for visible light oxygen generation from water [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131: 13833-13839. |
| 29 | Zhao Y, Chen P, Zhang B, et al. Highly dispersed TiO6 units in a layered double hydroxide for water splitting [J]. Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18: 11949–11958. |
| 30 | Zhao Y, Li B, Wang Q, et al. NiTi-layered double hydroxides nanosheets as efficient photocatalysts for oxygen evolution from water using visible light [J]. Chem. Sci., 2014, 5(3): 951-958. |
| 31 | Li B, Zhao Y, Zhang S, et al. Visible-light-responsive photocatalysts toward water oxidation based on NiTi-layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide composite materials [J]. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(20): 10233-10239. |
| 32 | Gunjakar J L, Kim T W, Kim H N, et al. Mesoporous layer-by-layer ordered nanohybrids of layered double hydroxide and layered metal oxide: highly active visible light photocatalysts with improved chemical stability [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(38): 14998-15007. |
| 33 | Wang C, Ma B, Xu S, et al. Visible-light-driven overall water splitting with a largely-enhanced efficiency over a Cu2O@ZnCr-layered double hydroxide photocatalyst [J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 32: 463-469. |
| 34 | Wang C, Ma B, Cao X, et al. Bridge-type interface optimization on a dual-semiconductor heterostructure toward high performance overall water splitting [J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(17): 7871-7876. |
| 35 | Zhou P, Wang Y, Xie C, et al. Acid-etched layered double hydroxides with rich defects for enhancing the oxygen evolution reaction [J]. Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(86): 11778-11781. |
| 36 | Huang L, Chen R, Xie C, et al. Rapid cationic defect and anion dual-regulated layered double hydroxides for efficient water oxidation [J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(28): 13638-13644. |
| 37 | Gao Z, Liu J, Chen X, et al. Engineering NiO/NiFe LDH intersection to bypass scaling relationship for oxygen evolution reaction via dynamic tridimensional adsorption of intermediates [J]. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(11): e1804769. |
| 38 | Zhang J, Liu J, Xi L, et al. Single-atom Au/NiFe layered double hydroxide electrocatalyst: probing the origin of activity for oxygen evolution reaction [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(11): 3876-3879. |
| 39 | Xiong X, Cai Z, Zhou D, et al. A highly-efficient oxygen evolution electrode based on defective nickel-iron layered double hydroxide [J]. Sci. China Mater., 2018, 61(7): 939-947. |
| 40 | 李天, 郝晓杰, 白莎, 等. 单层类水滑石纳米片的可控合成及规模生产展望[J]. 物理化学学报, 2020, 36: 1912005. |
| Li T, Hao X J, Bai S, et al. Controllable synthesis and scale-up production prospect of monolayer layered double hydroxide nanosheets[J]. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2020, 36: 1912005. | |
| 41 | Zhao Y, Zhang X, Jia X, et al. Sub-3 nm ultrafine monolayer layered double hydroxide nanosheets for electrochemical water oxidation [J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(18):1703585. |
| 42 | Zhu H, Zhang J, Yanzhang R, et al. When cubic cobalt sulfide meets layered molybdenum disulfide: a core-shell system toward synergetic electrocatalytic water splitting [J]. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(32): 4752-4759. |
| 43 | Li Y, Zhang H, Jiang M, et al. Ternary NiCoP nanosheet arrays: an excellent bifunctional catalyst for alkaline overall water splitting [J]. Nano Res., 2016, 9(8): 2251-2259. |
| 44 | Zhou L, Jiang S, Liu Y, et al. Ultrathin CoNiP@layered double hydroxides core–shell nanosheets arrays for largely enhanced overall water splitting [J]. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(2): 623-631. |
| 45 | Jia X, Zhao Y, Chen G, et al. Ni3FeN nanoparticles derived from ultrathin NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheets: an efficient overall water splitting electrocatalyst[J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(10): 1502585. |
| 46 | Xiao K, Zhou L, Shao M, et al. Fabrication of (Ni,Co)0.85Se nanosheet arrays derived from layered double hydroxides toward largely enhanced overall water splitting [J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(17): 7585-7591. |
| 47 | Yang H, Chen Z, Guo P, et al. B-doping-induced amorphization of LDH for large-current-density hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 261: 118240. |
| 48 | Fan H, Chen W, Chen G, et al. Plasma-heteroatom-doped Ni-V-Fe trimetallic phospho-nitride as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalyst [J]. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 268: 118440. |
| 49 | Artero V, Chavarot-Kerlidou M, Fontecave M, et al. Splitting water with cobalt [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(32): 7238-7266. |
| 50 | Zhang R, Shao M, Xu S, et al. Photo-assisted synthesis of zinc-iron layered double hydroxides/TiO2 nanoarrays toward highly-efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting [J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 33: 21-28. |
| 51 | Liu J, Xu S, Li Y, et al. Facet engineering of WO3 arrays toward highly efficient and stable photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from natural seawater [J]. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 264: 118540. |
| 52 | Guo J, Mao C, Zhang R, et al. Reduced titania@layered double hydroxide hybrid photoanodes for enhanced photoelectrochemical water oxidation [J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(22): 11016-11025. |
| 53 | Shao M, Ning F, Wei M, et al. Hierarchical nanowire arrays based on ZnO core-layered double hydroxide shell for largely enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting [J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(5): 580-586. |
| 54 | Long X, Wang C, Wei S, et al. Layered double hydroxide onto perovskite oxide-decorated ZnO nanorods for modulation of carrier transfer behavior in photoelectrochemical water oxidation [J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(2): 2452-2459. |
| 55 | Hage R, Lienke A. Applications of transition-metal catalysts to textile and wood-pulp bleaching [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 45(2): 206-222. |
| 56 | Campos-Martin J M, Blanco-Brieva G, Fierro J L, et al. Hydrogen peroxide synthesis: an outlook beyond the anthraquinone process [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(42): 6962-6984. |
| 57 | Cho S, Jang J W, Park Y B, et al. An exceptionally facile method to produce layered double hydroxides on a conducting substrate and their application for solar water splitting without an external bias [J]. Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(7): 2301-2307. |
| 58 | Bi S, Li J, Zhong Q, et al. Low-cost CoFe2O4/biomass carbon hybrid from metal-enriched sulfate reducing bacteria as an electrocatalyst for water oxidation [J]. RSC Adv., 2018, 8(40): 22799-22805. |
| 59 | Jafari Foruzin L, Rezvani Z, Nejati K, et al. High quantum efficiency of photocatalytic water oxidation over the TiO2/MMO nanocomposite under visible-light irradiation [J]. J. Mol. Liq., 2019, 12: 2452-2459. |
| 60 | Wang R, Pan K, Han D, et al. Solar-driven H2O2 generation from H2O and O2 using earth-abundant mixed-metal oxide@carbon nitride photocatalysts [J]. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(17): 2470-2479. |
| 61 | Han D, Xiang X, Yang J, et al. In-situ conversion and catalytic properties of mixed-metal oxide catalysts for photosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide [J]. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2017, 47(4): 465-473. |
| 62 | Sharma A S, Kaur H, Shah D, et al. Selective oxidation of alcohols by supported gold nanoparticles: recent advances [J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(34): 28688-28727. |
| 63 | Cho S H, Kim J Y, Kwak J. Recent advances in the transition metal-catalyzed two-fold oxidative C—H bond activation strategy for C—C and C—N bond formation [J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(10): 5068-5083. |
| 64 | Galvis H M T, de Jong K P. Catalysts for production of lower olefins from synthesis gas: a review [J]. ACS Catal., 2013, 3(9): 2130-2149. |
| 65 | Yang C, Zhao H, Hou Y, et al. Fe5C2 nanoparticles: a facile bromide-induced synthesis and as an active phase for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(38): 15814-15821. |
| 66 | Gao W, Zhao Y, Chen H, et al. Core-shell Cu@(CuCo-alloy)/Al2O3 catalysts for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas [J]. Green Chem., 2015, 17(3): 1525-1534. |
| 67 | Eggenhuisen T M, Munnik P, Talsma H, et al. Freeze-drying for controlled nanoparticle distribution in Co/SiO2 Fischer-Tropsch catalysts [J]. J. Catal., 2013, 297: 306-313. |
| 68 | Hirsa M, Johannes H, Chaitanya B, et al. Supported iron nanoparticles as catalysts for sustainable production of lower olefins [J]. Science, 2012, 335: 835-838. |
| 69 | Li Y, Gao W, Peng M, et al. Interfacial Fe5C2-Cu catalysts toward low-pressure syngas conversion to long-chain alcohols [J]. Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1): 61-68. |
| 70 | Zhao Y, Zhao B, Liu J, et al. Oxide-modified nickel photocatalysts for the production of hydrocarbons in visible light [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(13): 4215-4219. |
| 71 | Li Z, Liu J, Zhao Y, et al. Co-based catalysts derived from layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets for the photothermal production of light olefins [J]. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(31): e1800527. |
| 72 | Zhao Y, Li Z, Li M, et al. Reductive transformation of layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets to Fe-based heterostructures for efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogenation of CO [J]. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30: e1803127. |
| 73 | Chen G, Gao R, Zhao Y, et al. Alumina-supported CoFe alloy catalysts derived from layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photothermal CO2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons [J]. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(3): 1704663. |
| 74 | Guo Y, Hu J, Wan L, et al. Nanostructured materials for electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices [J]. Adv. Mater., 2008, 20(15): 2878-2887. |
| 75 | Wallace G G, Chen J, Li D, et al. Nanostructured carbon electrodes [J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(18): 3553-3562. |
| 76 | Shao M, Ning F, Zhao J, et al. Hierarchical layered double hydroxide microspheres with largely enhanced performance for ethanol electrooxidation [J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(28): 3513-3518. |
| 77 | Li L, Dou L, Zhang H, et al. Layered double hydroxide supported gold nanoclusters by glutathione-capped Au nanoclusters precursor method for highly efficient aerobic oxidation of alcohols [J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(7): 3753-3763. |
| 78 | Fang W, Zhang Q, Chen J, et al. Gold nanoparticles on hydrotalcites as efficient catalysts for oxidant-free dehydrogenation of alcohols [J]. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(9): 1547-1549. |
| 79 | Wang C, Xie Z, de Krafft K E, et al. Doping metal-organic frameworks for water oxidation, carbon dioxide reduction, and organic photocatalysis [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(34): 13445-13454. |
| 80 | Fu Y, Sun D, Chen Y, et al. An amine-functionalized titanium metal-organic framework photocatalyst with visible-light-induced activity for COL reduction [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(14): 3364-3367. |
| 81 | Li Q, Li X, Wageh S, et al. CdS/graphene nanocomposite photocatalysts [J]. Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5: 1500010. |
| 82 | Zhang J, Wang Y, Jin J, et al. Efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and enhanced photostability of core/shell CdS/g-C3N4 nanowires [J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(20): 10317-10324. |
| 83 | 张晓晴,徐艳,杨春辉,等.原位共沉淀法制备Ni-Mg-Al-LDHs/γ-Al2O3催化前驱体在甲烷二氧化碳重整反应体系中的性能评价[J]. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(5): 948-954. |
| Zhang X Q, Xu Y, Yang C H, et al. In-situ co-precipitation of Ni-Mg-Al-LDH catalytic precursor on γ-Al2O3 for dry reforming of methane: synthesis and evaluation [J]. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2015, 31(5): 948-954. | |
| 84 | Zhu M, Ge Q, Zhu X. Catalytic reduction of CO2 to CO via reverse water gas shift reaction: recent advances in the design of active and selective supported metal catalysts [J]. Trans. Tianjin Univ., 2020,26(3): 172-187. |
| 85 | Zhao Y, Chen G, Bian T, et al. Defect-rich ultrathin ZnAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photoreduction of CO2 to CO with water [J]. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(47): 7824-7831. |
| 86 | Tan L, Xu S M, Wang Z, et al. Highly selective photoreduction of CO2 with suppressing H2 evolution over monolayer layered double hydroxide under irradiation above 600 nm [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(34): 11860-11867. |
| 87 | Zhao Y, Liu C, Wang C, et al. Sulfur vacancy-promoted highly selective electrosynthesis of functionalized aminoarenes via transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes with H2O over a Co3S4-x nanosheet cathode [J]. CCS Chem., 2020, 2: 507-515. |
| 88 |
Wu Y, Liu C, Wang C, et al. Selective transfer semihydrogenation of alkynes with H2O (D2O) as the H (D) source over a Pd-P cathode [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020. doi: 10.1002/anie.202009757.
DOI URL |
| 89 | Wang Z, Xu S, Tan L, et al. 600 nm-driven photoreduction of CO2 through the topological transformation of layered double hydroxides nanosheets [J]. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2020, 270: 11884. |
| 90 | Hao X, Tan L, Xu Y, et al. Engineering active Ni sites in ternary layered double hydroxide nanosheets for a highly selective photoreduction of CO2 to CH4 under irradiation above 500 nm [J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2020, 59(7): 3008-3015. |
| 91 | Bai S, Wang Z, Tan L, et al. 600 nm irradiation-induced efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction by ultrathin layered double hydroxide nanosheets [J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2020, 59(13): 5848-5857. |
| 92 | Davis B. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: reaction mechanisms for iron catalysts [J]. Catal. Today, 2009, 141(1/2): 25-33. |
| 93 | Wang X, Wang Z, Bai Y, et al. Tuning the selectivity of photoreduction of CO2 to syngas over Pd/layered double hydroxide nanosheets under visible light up to 600 nm [J]. J. Energy Chem., 2020, 46: 1-7. |
| 94 | Qiu C, Hao X, Tan L, et al. 500 nm induced tunable syngas synthesis from CO2 photoreduction by controlling heterojunction concentration [J]. Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(40): 5354-5357. |
| 95 | Kipkorip P, Tan L, Ren J, et al. Intercalation effect in NiAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for CO2 reduction under visible light [J]. Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2020, 36(1): 127-133. |
| 96 |
Tan L, Kipkorip P, Ren J, et al. Photocatalytic syngas synthesis from CO2 to H2O using ultrafine CeO2-decorated layered double hydroxide nanosheets under visible light up to 600 nm [J]. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng., 2020. doi: 10.1007/S11705-020-1947-4.
DOI URL |
| 97 | Zhang R, Shao M, Li Z, et al. Photoelectrochemical catalysis toward selective anaerobic oxidation of alcohols [J]. Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23(34): 8142-8147. |
| 98 | Liu J, Li J, Shao M, et al. Directed synthesis of SnO2@BiVO4/Co-Pi photoanode for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting and urea oxidation [J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(11): 6327-6336. |
| 99 | Li J, Xu Y, Ding Z, et al. Photocatalytic selective oxidation of benzene to phenol in water over layered double hydroxide: a thermodynamic and kinetic perspective [J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 388: 124248. |
| 100 | You B, Jiang N, Liu X, et al. Simultaneous H2 generation and biomass upgrading in water by an efficient noble-metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst [J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(34): 9913-9917. |
| 101 | You B, Liu X, Jiang N, et al. A general strategy for decoupled hydrogen production from water splitting by integrating oxidative biomass valorization [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(41): 13639-13646. |
| 102 | Liu W J, Dang L, Xu Z, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with NiFe layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheet catalysts [J]. ACS Catal., 2018, 8(6): 5533-5541. |
| [1] | Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [2] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | Jie CHEN, Yongsheng LIN, Kai XIAO, Chen YANG, Ting QIU. Study on catalytic synthesis of sec-butanol by tunable choline-based basic ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [4] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [5] | Xin YANG, Xiao PENG, Kairu XUE, Mengwei SU, Yan WU. Preparation of molecularly imprinted-TiO2 and its properties of photoelectrocatalytic degradation of solubilized PHE [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [6] | Feifei YANG, Shixi ZHAO, Wei ZHOU, Zhonghai NI. Sn doped In2O3 catalyst for selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [7] | Kaixuan LI, Wei TAN, Manyu ZHANG, Zhihao XU, Xuyu WANG, Hongbing JI. Design of cobalt-nitrogen-carbon/activated carbon rich in zero valent cobalt active site and application of catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [8] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [9] | Yuming TU, Gaoyan SHAO, Jianjie CHEN, Feng LIU, Shichao TIAN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of calcium-based catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [10] | Qiyu ZHANG, Lijun GAO, Yuhang SU, Xiaobo MA, Yicheng WANG, Yating ZHANG, Chao HU. Recent advances in carbon-based catalysts for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [11] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [12] | Yajie YU, Jingru LI, Shufeng ZHOU, Qingbiao LI, Guowu ZHAN. Construction of nanomaterial and integrated catalyst based on biological template: a review [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| [13] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [14] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [15] | Pan LI, Junyang MA, Zhihao CHEN, Li WANG, Yun GUO. Effect of the morphology of Ru/α-MnO2 on NH3-SCO performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||