化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3007-3017.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220412
收稿日期:2022-03-24
修回日期:2022-05-11
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
杨颖,宋兴福
作者简介:苏晨昱(1997—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Chenyu SU1,2( ),Ying YANG1,2(
),Ying YANG1,2( ),Xingfu SONG1,2(
),Xingfu SONG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-03-24
Revised:2022-05-11
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Ying YANG,Xingfu SONG
摘要:
中南半岛岩盐矿提钾老卤中溴离子含量约为3000 mg/L,是极具价值的制溴原料。岩盐矿伴生溴资源的有效利用,对提高岩盐矿资源综合利用价值,缓解我国溴资源短缺现状,具有经济、社会及环境多重意义。通过三电极体系线性扫描伏安法与电氧化实验,对含溴模拟卤水中溴离子的氧化速率以及氯离子浓度、电极的有效面积、搅拌速率对其的影响进行研究。结果表明1.150 V为合适的溴离子选择性氧化的电极电位,且反应符合一级反应动力学规律。针对氯离子浓度为280 g/L的岩盐矿提钾老卤,石墨电极的有效面积50.18 cm2,搅拌速率400 r/min时溴离子电氧化的速率最快,反应速率常数为0.3042 h-1,电氧化8 h后溴转化率为91.9%。
中图分类号:
苏晨昱, 杨颖, 宋兴福. 岩盐矿提钾老卤中溴离子选择性电氧化过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3007-3017.
Chenyu SU, Ying YANG, Xingfu SONG. Selective electro-oxidation of bromide ion in potassium-extracted brine from rock salt mines[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3007-3017.
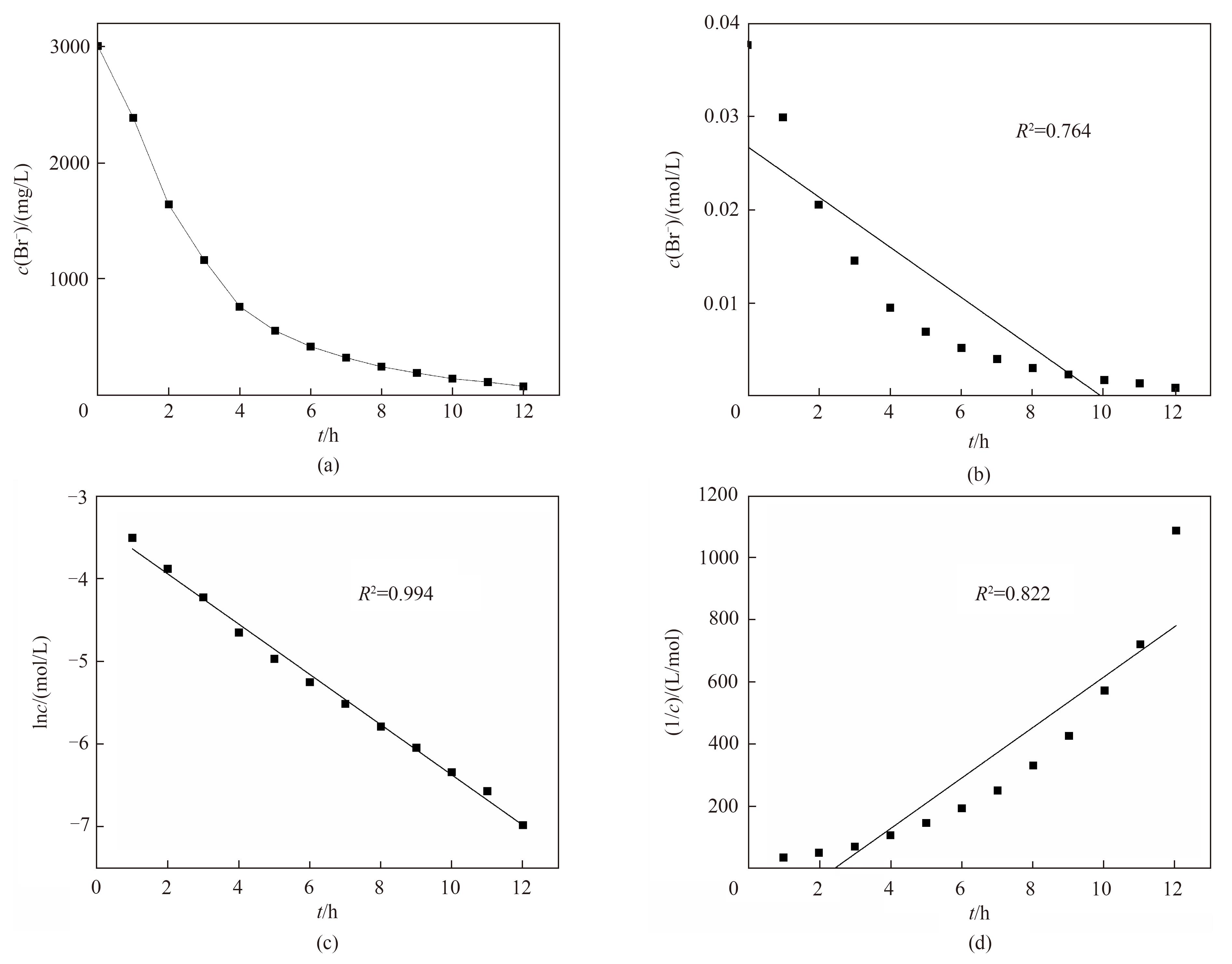
图4 (a)阳极室中溴离子浓度与电氧化时间的关系;(b)零级反应动力学模型拟合;(c)一级反应动力学模型拟合;(d)二级反应动力学模型拟合
Fig.4 (a) Changes of Br- concentration with reaction time in anode chamber;Changes of (b) c, (c) lnc and (d) 1/c with reaction time

图5 不同氯离子浓度下溴离子浓度(a)和溴转化率(b)随时间的变化
Fig.5 Changes of Br- concentration (a) and bromine conversion (b) with reaction time under different Cl- concentrations
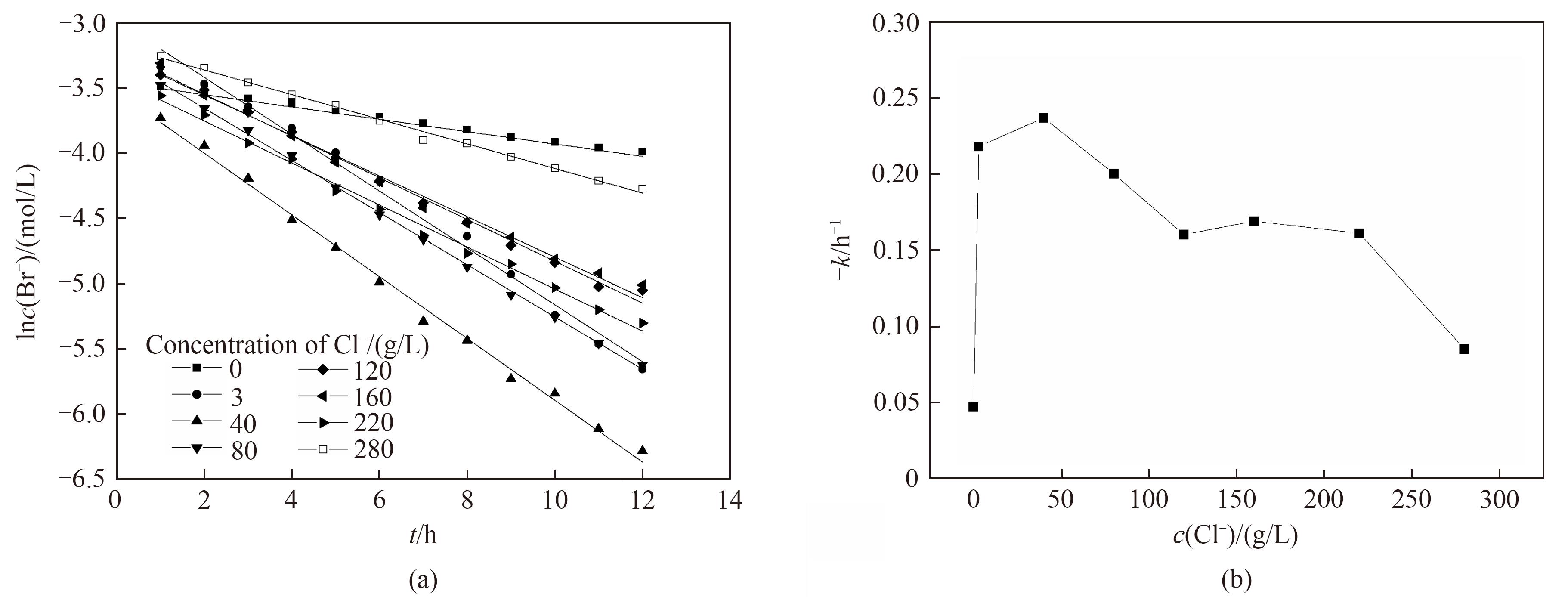
图6 不同氯离子浓度下电氧化溴离子的一级反应动力学拟合(a)和一级反应动力学反应速率常数(b)
Fig.6 Kinetic fitting of first-order reaction (a) and change of -k (b) for electro-oxidation of Br- at different Cl- concentrations
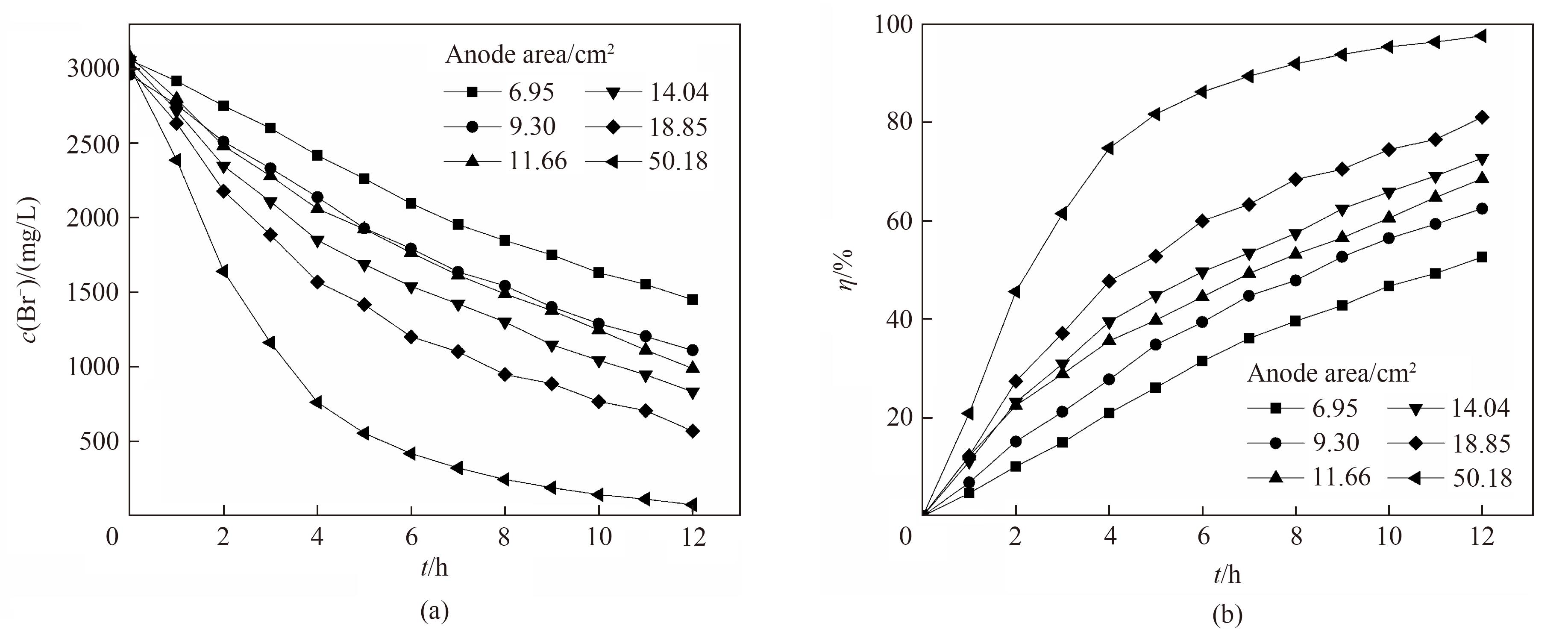
图8 不同阳极石墨电极有效面积下电氧化溴离子浓度(a)和溴转化率(b)随时间的变化关系
Fig.8 Change of Br- concentration (a) and bromine conversion (b) with reaction time under different anode electrode effective area

图9 不同阳极石墨电极有效面积下电氧化溴离子的一级反应动力学拟合(a)和一级反应动力学反应速率常数(b)
Fig.9 Kinetic fitting of first-order reaction (a) and change of -k (b) for electro-oxidation of Br- at different anode electrode effective area
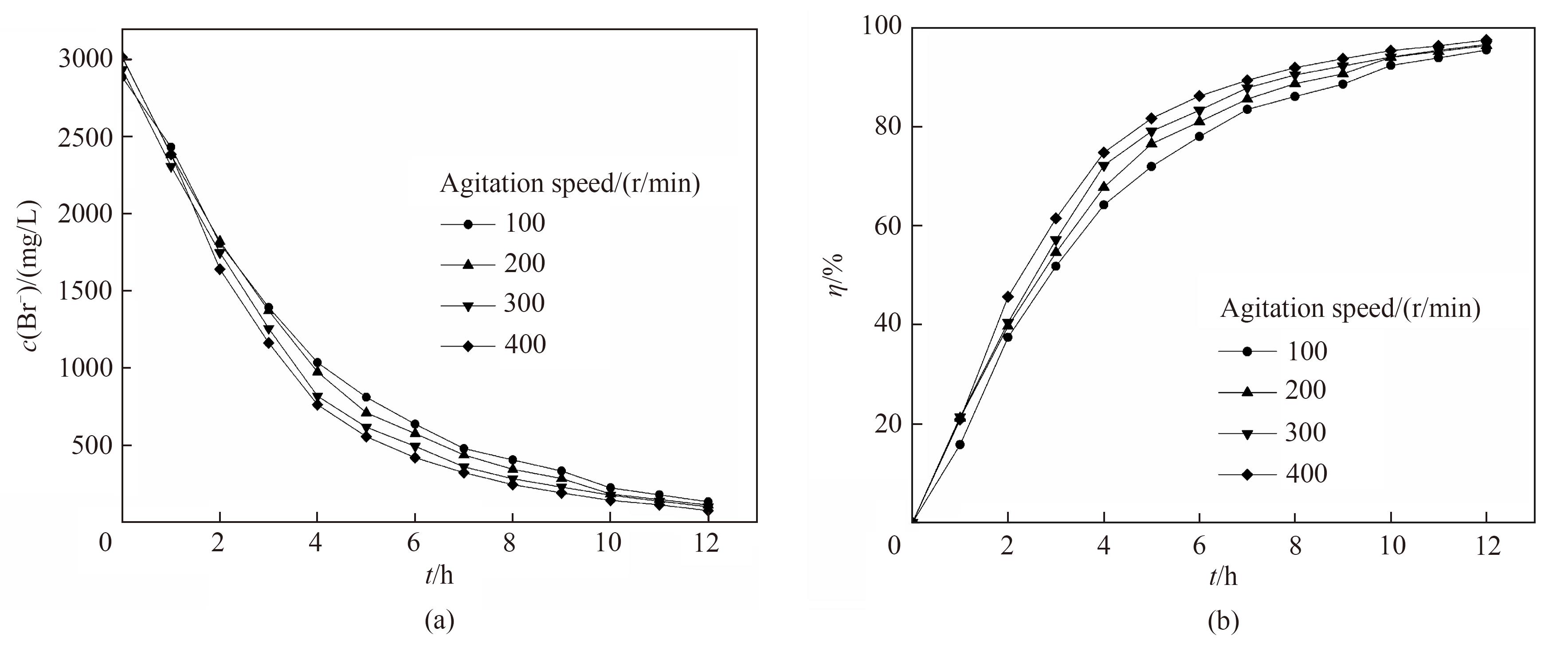
图10 不同转速下电氧化溴离子浓度(a)和溴转化率(b)随时间的变化关系
Fig.10 Change of Br- concentration (a) and bromine conversion (b) with reaction time under the different rotating speed
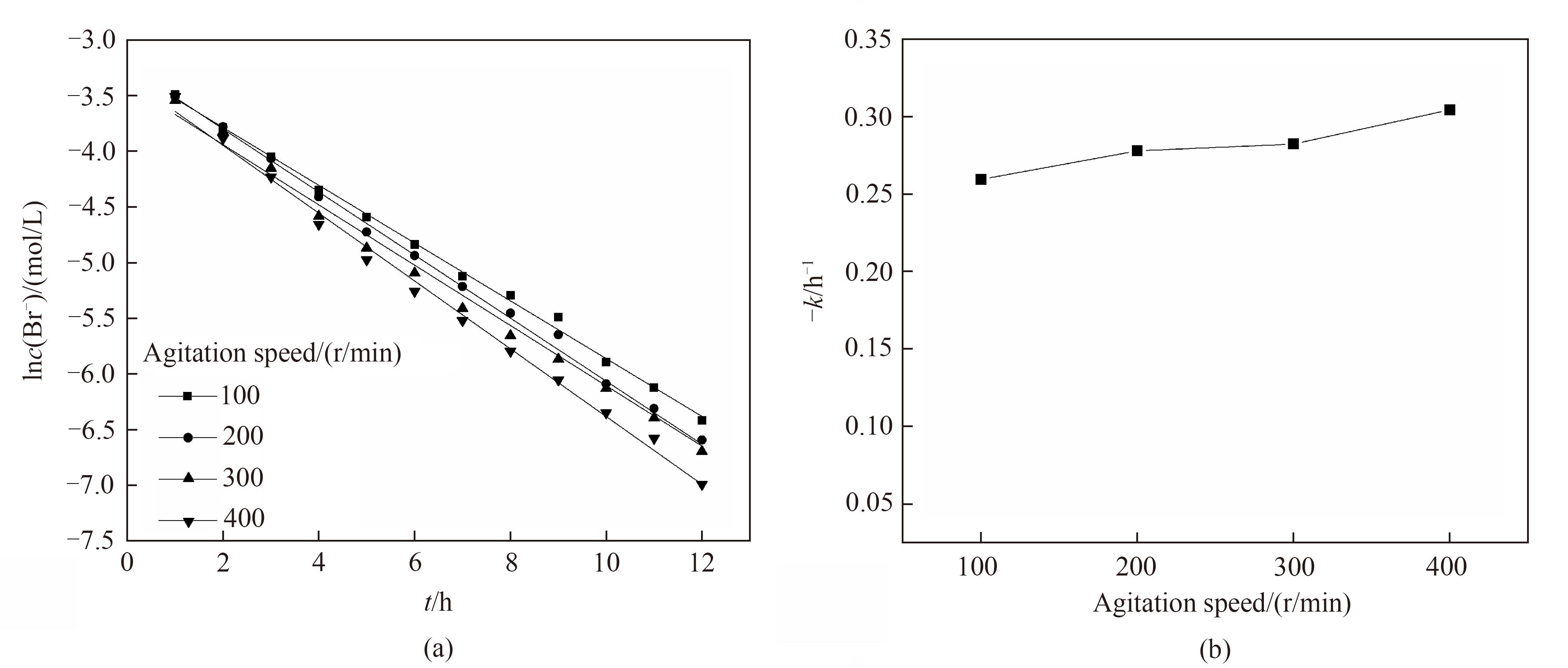
图11 不同转子转速下电氧化溴离子的一级反应动力学拟合(a)和一级反应动力学反应速率常数(b)
Fig.11 Kinetic fitting of first-order reaction (a) and change of -k (b) for electro-oxidation of Br- at different rotating speed
| 1 | 陈向楠, 王海增. 溴素资源与产业发展分析[J]. 盐业与化工, 2013, 42(6): 4-7. |
| Chen X N, Wang H Z. Bromine resource and analysis of the industry development[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2013, 42(6): 4-7. | |
| 2 | 柴子华, 李明明. 我国溴工业生产技术现状与展望[J]. 盐科学与化工, 2018, 47(6): 1-4. |
| Chai Z H, Li M M. Domestic manufacturing process and expectation of bromine industry[J]. Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(6): 1-4. | |
| 3 | 中华人民共和国海关总署. 海关统计数据在线查询平台[EB/OL].[2022-03-23]. . |
| General Administration of Customs. P.R.China. Customs Statistics [EB/OL]. [2022-03-23]. . | |
| 4 | 王刚, 李建国. 盐化工工艺学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016. |
| Wang G, Li J G. Salt Chemical Technology[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016. | |
| 5 | 朱延浙, 吴军, 严城民. 老挝钾盐资源现状及对策建议[J]. 资源与产业, 2016, 18(2): 44-47. |
| Zhu Y Z, Wu J, Yan C M. Actuality of and approaches to Laos's potash resources[J]. Resources & Industries, 2016, 18(2): 44-47. | |
| 6 | 李建业. 浅析老挝钾矿资源开发现状[J]. 盐业与化工, 2016, 45(10): 5-9. |
| Li J Y. Analysis on the current situation in Laos potash resource development[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(10): 5-9. | |
| 7 | 秦占杰. 呵叻高原钾盐矿床物源及其沉积演化的地球化学研究[D]. 西宁: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院青海盐湖研究所), 2019. |
| Qin Z J. Geochemical research on the provenance and sedimentary characteristics of potash deposits in the Khorat Plateau[D]. Xining: Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. | |
| 8 | Stewart L C. Commercial extraction of bromine from sea water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2002, 26(4): 361-369. |
| 9 | 王寿武, 卢伯南. 溴素生产现状及展望[J]. 中国井矿盐, 2004, 35(2): 9-12. |
| Wang S W, Lu B N. Current situation and prospect of elementary bromine production[J]. China Well and Rock Salt, 2004, 35(2): 9-12. | |
| 10 | 李萌. 海水提溴技术的研究与发展[J]. 盐业与化工, 2014, 43(11): 1-4. |
| Li M. Research and development of the technique about bromine extracting from seawater[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2014, 43(11): 1-4. | |
| 11 | 詹进先. 试论威远气田水提溴技术[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 1996, 25(4): 239-242, 248. |
| Zhan J X. Discussion on bromine extraction from Weiyuan gas field water[J]. Oil & Gas Chemicals, 1996, 25(4): 239-242, 248. | |
| 12 | 张力军, 王薇, 王修林. 溴素生产技术及溴系列产品的开发[J]. 海洋科学, 1998, 22(5): 20-23. |
| Zhang L J, Wang W, Wang X L. Introduction to technique of manufacturing bromine and prospecting development trend in bromined products[J]. Marine Sciences, 1998, 22(5): 20-23. | |
| 13 | 朱昌洛, 寇建军. 树脂吸附法由卤水中提溴[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2003(5): 13-16. |
| Zhu C L, Kou J J. Extraction of bromine from brine by RIP method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2003(5): 13-16. | |
| 14 | 袁纯怡, 孙玉柱, 杨颖, 等. D301树脂动态吸附溴离子过程探究及模型拟合[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(6): 655-666. |
| Yuan C Y, Sun Y Z, Yang Y, et al. Performance and modelling of bromide dynamic adsorption onto D301 anion exchange resin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(6): 655-666. | |
| 15 | 孙维缜. 强碱性阴离子交换树脂用于卤水提溴[J]. 水处理技术, 1985, 11(4): 44-47. |
| Sun W Z. Extraction of bromine from brine by strongly basic anion exchange resin process[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 1985, 11(4): 44-47. | |
| 16 | Qi Z, Cussler E L. Bromine recovery with hollow fiber gas membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1985, 24(1): 43-57. |
| 17 | Singh V, Rhinehart R R, Narayan R S, et al. Transport analysis of hollow fiber gas separation membranes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1995, 34(12): 4472-4478. |
| 18 | Nakashio F. Recent advances in separation of metals by liquid surfactant membranes[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 1993, 26(2): 123-133. |
| 19 | 李海民, 程怀德, 张全有. 卤水资源开发利用技术述评(续完)[J]. 盐湖研究, 2004, 12(1): 56,62-72. |
| Li H M, Cheng H D, Zhang Q Y. Evaluation of the technologies of comprehensive utilizationand exploitation brine resources[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2004, 12(1): 56,62-72. | |
| 20 | Cohen I, Shapira B, Avraham E, et al. Bromide ions specific removal and recovery by electrochemical desalination[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(11): 6275-6281. |
| 21 | 武爱莲, 孙彦平. 溴离子在旋转圆盘电极上氧化动力学模型[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 1999, 30(1): 36-39. |
| Wu A L, Sun Y P. A model of bromide oxidation on a rotating disk electrode[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 1999, 30(1): 36-39. | |
| 22 | Sun M, Lowry G V, Gregory K B. Selective oxidation of bromide in wastewater brines from hydraulic fracturing[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(11): 3723-3731. |
| 23 | Zhang X, Ji Z Y, Liu F, et al. Investigation of electrochemical oxidation technology for selective bromine extraction in comprehensive utilization of concentrated seawater[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 248: 117108. |
| 24 | 张晓, 纪志永, 汪婧, 等. 电氧化法地下卤水提溴探究及条件优化[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2123-2131. |
| Zhang X, Ji Z Y, Wang J, et al. Exploration and optimization of extraction process of bromine from underground brine by electrooxidation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2123-2131. | |
| 25 |
王丹, 赵方, 于建国, 等. 微通道中萃取法分离提取溴素[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, DOI:10.14135/j.cnki.1006-3080.20210617003 .
DOI |
|
Wang D, Zhao F, Yu J G, et al. Separation and extraction of bromine by microchannel extraction[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2021,DOI:10.14135/j.cnki.1006-3080.20210617003 .
DOI |
|
| 26 | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 化学试剂 溴: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Chemical reagent—bromine: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011. | |
| 27 | Fogler H S. Elements of chemical reaction engineering[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1987, 42(10): 2493. |
| 28 | Haynes W M, Lide D R, Bruno T J. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics[M]. CRC Press, 2016. |
| 29 | 屈红强, 舒尊哲. 无机化学[M]. 成都: 四川大学出版社, 2015. |
| Qu H Q, Shu Z Z. Inorganic Chemistry[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan University Press, 2015. | |
| 30 | Li S F. Reaction Engineering[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016. |
| 31 | 刘国桢. 现代氯碱技术手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2018. |
| Liu G Z. Modern Chlor-alkali Technical Manual[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2018. | |
| 32 | 许晓慧. 海盐生产及苦卤利用技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017. |
| Xu X H. Sea Salt Production and Bittern Utilization Technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2017. | |
| 33 | 郭晓俊, 袁俊生, 赵颖颖, 等. 浓海水制备液体盐过程中空气吹出法除溴的研究[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 2017, 46(3): 73-77. |
| Guo X J, Yuan J S, Zhao Y Y, et al. On removal of bromine by air blowing method in the preparing course of liquid salt from brine[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2017, 46(3): 73-77. | |
| 34 | 杨金水, 成新云, 滕克山. 浅谈冬季制溴生产工艺[J]. 盐业与化工, 2012, 41(8): 20-22. |
| Yang J S, Cheng X Y, Teng K S. Brief discussion on bromine production technology in winter[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2012, 41(8): 20-22. |
| [1] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [2] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [3] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [4] | 胡超, 董玉明, 张伟, 张红玲, 周鹏, 徐红彬. 浓硫酸活化五氧化二钒制备高浓度全钒液流电池正极电解液[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [5] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [6] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [7] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [8] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [9] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [10] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [11] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [12] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [13] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [14] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [15] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号