化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3174-3181.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220097
赵继昊1( ),唐伟强1,徐小飞1(
),唐伟强1,徐小飞1( ),赵双良1,2,贺炅皓3
),赵双良1,2,贺炅皓3
收稿日期:2022-01-18
修回日期:2022-04-12
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
徐小飞
作者简介:赵继昊(1996—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Jihao ZHAO1( ),Weiqiang TANG1,Xiaofei XU1(
),Weiqiang TANG1,Xiaofei XU1( ),Shuangliang ZHAO1,2,Jionghao HE3
),Shuangliang ZHAO1,2,Jionghao HE3
Received:2022-01-18
Revised:2022-04-12
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Xiaofei XU
摘要:
由高分子、填料、键合剂及各种功能助剂组成的高分子复合材料广泛应用于轮胎、含能材料、医疗、环保、建筑、交通等行业。键合剂在填料表面的吸附特性对高分子复合材料的性能有重要影响。分别以未改性的高氯酸铵、炭黑和二氧化硅填料为对象,利用第一性原理计算评估了五种键合剂分子,即三乙醇胺(TEA)、三氟化硼三乙醇胺络合物(T313)、N,N'-二邻甲苯胍(DOTG)、N,N'-二苯基硫脲(DPTU)和二苯胍(DPG),在填料表面的吸附能。计算结果表明,随着填料基底层数的增加,吸附能逐渐增加,最后趋于一个稳定值。其中TEA和T313键合剂在高氯酸铵表面的吸附能为-0.84~-1.37 eV;DOTG、DPTU和DPG在炭黑表面的吸附能为-1.01~-1.29 eV;在二氧化硅表面的吸附能为-0.87~-0.94 eV;在接枝羟基的二氧化硅上的吸附能为-1.16~-1.36 eV。依次考察了单层炭黑点缺陷(单空位缺陷、双空位缺陷、Stone-Wales缺陷)和二氧化硅表面接枝羟基对吸附能的影响,发现单空位和双空位缺陷对吸附能影响不大,而Stone-Wales缺陷和二氧化硅接枝羟基显著增加吸附能。
中图分类号:
赵继昊, 唐伟强, 徐小飞, 赵双良, 贺炅皓. 高分子复合材料中键合剂在不同纳米填料表面的吸附能计算[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3174-3181.
Jihao ZHAO, Weiqiang TANG, Xiaofei XU, Shuangliang ZHAO, Jionghao HE. Adsorption energy of bonding agent on nano-filler in polymer composites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3174-3181.

图2 五种键合剂分子的分子结构与静电势分布: (a) TEA; (b) T313; (c) DPG; (d) DPTU; (e) DOTG(1 cal=4.184 J)
Fig.2 Molecular structure and electrostatic potential distribution of five bond agents: (a) TEA; (b) T313; (c) DPG; (d) DPTU; (e) DOTG
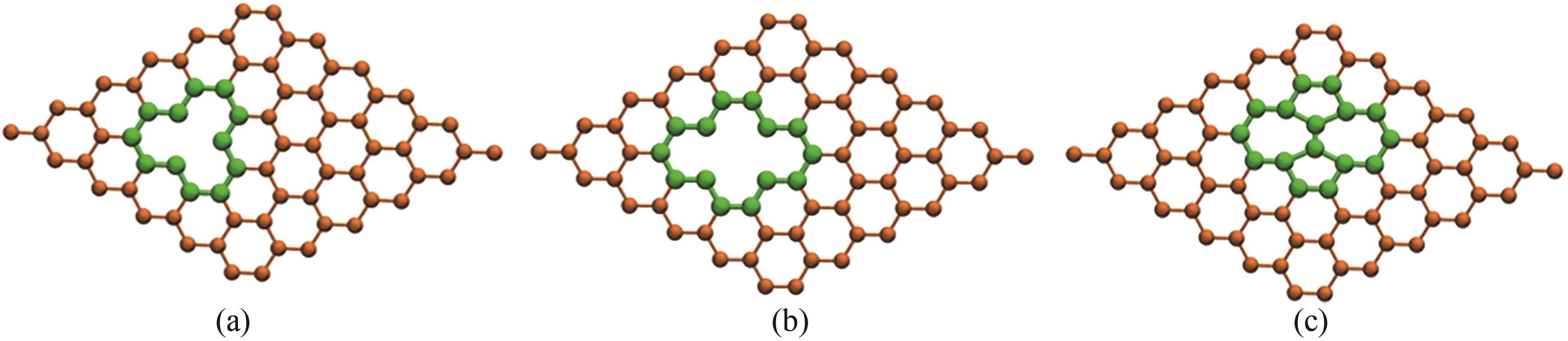
图7 炭黑表面缺陷模型: (a) 单空位缺陷;(b) 双空位缺陷;(c) Stone-Wales缺陷
Fig.7 Carbon black surface defect model: (a) single vacancy defect; (b) divacancy defect; (c) Stone-Wales defect
| 缺陷类型 | 吸附能/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DPG | DPTU | DOTG | |
| 无缺陷 | -0.99 | -1.12 | -1.28 |
| 单空位 | -0.99 | -1.12 | -1.27 |
| 双空位 | -0.97 | -1.09 | -1.26 |
| Stone-Wales | -1.01 | -1.14 | -1.30 |
表1 有机分子与不同缺陷类型炭黑的吸附能
Table 1 Adsorption energy of organic molecules with different defect types of carbon black
| 缺陷类型 | 吸附能/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DPG | DPTU | DOTG | |
| 无缺陷 | -0.99 | -1.12 | -1.28 |
| 单空位 | -0.99 | -1.12 | -1.27 |
| 双空位 | -0.97 | -1.09 | -1.26 |
| Stone-Wales | -1.01 | -1.14 | -1.30 |
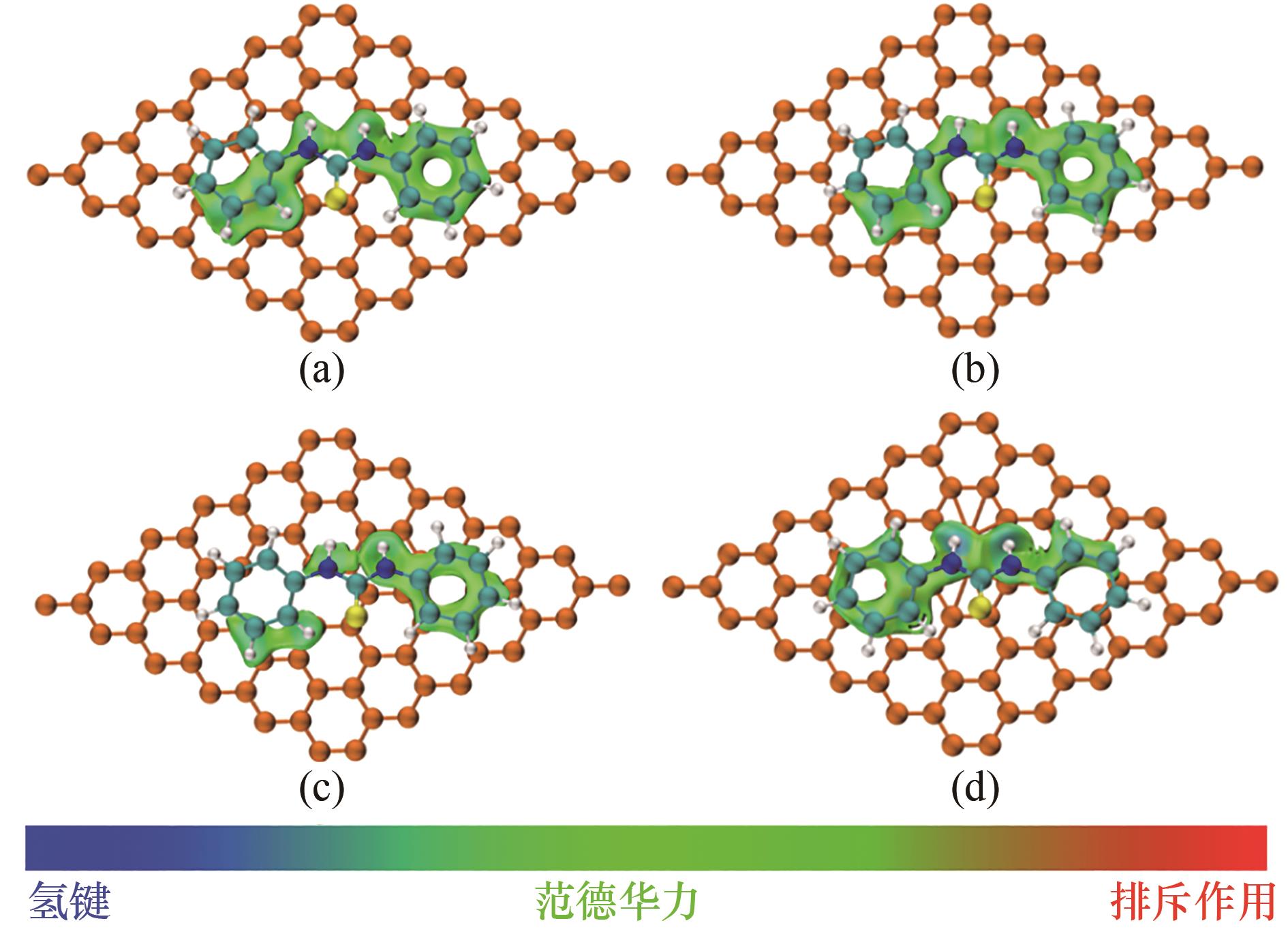
图8 DPTU在不同缺陷类型炭黑上的吸附: (a)无缺陷;(b)单空位缺陷;(c)双空位缺陷;(d)Stone-Wales缺陷
Fig.8 Adsorption of DPTU on carbon black with different defect types: (a) normal;(b) single vacancy defect;(c) divacancy defect;(d) Stone-Wales defect
| 基底类型 | 吸附能/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DPG | DPTU | DOTG | |
| 双层炭黑 | -1.01 | -1.14 | -1.29 |
| 双层SiO2 | -0.87 | -0.89 | -0.94 |
| 双层SiO2@OH | -1.16 | -1.20 | -1.35 |
表2 有机分子与不同基底的吸附能
Table 2 Adsorption energy of organic molecules with different substrates
| 基底类型 | 吸附能/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DPG | DPTU | DOTG | |
| 双层炭黑 | -1.01 | -1.14 | -1.29 |
| 双层SiO2 | -0.87 | -0.89 | -0.94 |
| 双层SiO2@OH | -1.16 | -1.20 | -1.35 |
| 1 | 郝丽娜, 张文广, 李莹莹. 功能高分子材料在工业领域中的应用及展望[J]. 天津化工, 2021, 35(5): 16-17. |
| Hao L N, Zhang W G, Li Y Y. Application and prostect of functional polymer materials in industrial field[J]. Tianjin Chemical Industry, 2021, 35(5): 16-17. | |
| 2 | Kosareva E K, Zharkov M N, Meerov D B, et al. HMX surface modification with polymers via sc-CO2 antisolvent process: a way to safe and easy-to-handle energetic materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131363. |
| 3 | 黄伟, 杨凯, 张乾, 等.橡胶补强填料中煤矸石活化改性的研究进展[J].洁净煤技术, 2022, 28(1): 166-174. |
| Huang W, Yang K, Zhang Q, et al. Research progress on activation modification of coal gangue as rubber reinforxing filler[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2022, 28(1): 166-174. | |
| 4 | 李鹏举, 吴晓辉, 卢咏来, 等. 氧化石墨烯/白炭黑纳米杂化填料在绿色轮胎胎面中的应用[J]. 合成橡胶工业, 2019, 42(4): 294-299. |
| Li P J, Wu X H, Lu Y L, et al. Application of graphene oxide/silica nano-hybrids in green tire tread[J]. China Synthetic Rubber Industry, 2019, 42(4): 294-299. | |
| 5 | Abdelhafiz M, Yehia M, Mostafa H E, et al. Self-catalyzed nanoscale ammonium perchlorate for advanced composite solid rocket propellant[J]. Nano Express, 2021, 2(3): 030008. |
| 6 | Pangamol P, Malee W, Yujaroen R, et al. Utilization of bagasse ash as a filler in natural rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber composites[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2018, 43(1): 221-227. |
| 7 | 解佳楠. 新型填料与炭黑、白炭黑的杂化改性及在橡胶中的应用[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2019. |
| Xie J N. New filler and hybrid modification with carbon black and silica and application in rubber[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science & Technology, 2019. | |
| 8 | Lu Y H, Chen W, Feng Y P, et al. Tuning the electronic structure of graphene by an organic molecule[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2009, 113(1): 2-5. |
| 9 | Tian X Q, Xu J B, Wang X M. Self-assembly of PTCDA ultrathin films on graphene: structural phase transition and charge transfer saturation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(49): 20917-20924. |
| 10 | Coletti C, Riedl C, Lee D S, et al. Charge neutrality and band-gap tuning of epitaxial graphene on SiC by molecular doping[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(23): 235401. |
| 11 | Vovusha H, Sanyal S, Sanyal B. Interaction of nucleobases and aromatic amino acids with graphene oxide and graphene flakes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(21): 3710-3718. |
| 12 | 王赛, 郭洋, 刘昌树. 二氧化硅作为新型环保吸附剂在食用油中的高效吸附作用[J]. 中国油脂, 2021, 46(8): 150-152. |
| Wang S, Guo Y, Liu C S. High efficient adsorption of silica as a new environmentally friendly adsorbent in edible oil[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2021, 46(8): 150-152. | |
| 13 | 张志强, 屈一新, 任慧. 纳米二氧化硅物理吸附乙醇的密度泛函研究[J]. 物理化学学报, 2006, 22(7): 820-825. |
| Zhang Z Q, Qu Y X, Ren H. Density functional theory studies on ethanol physisorption on ultrafine silica[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2006, 22(7): 820-825. | |
| 14 | Irfan Akay T, Toffoli D, Ustunel H. Combined effect of point defects and layer number on the adsorption of benzene and toluene on graphene[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 480: 1063-1069. |
| 15 | Gao H W, Liu Z J. DFT study of NO adsorption on pristine graphene[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(22): 13082-13091. |
| 16 | Li B, Ou P F, Wei Y L, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorption onto graphene: a DFT and AIMD study[J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2018, 11(5): 726. |
| 17 | Karlický F, Otyepková E, Lo R, et al. Adsorption of organic molecules to van der Waals materials: comparison of fluorographene and fluorographite with graphene and graphite[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2017, 13(3): 1328-1340. |
| 18 | Abuelela A M, Farag R S, Mohamed T A, et al. Ab initio study of the vibrational signatures for the covalent functionalization of graphene[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(38): 19489-19498. |
| 19 | Hassan M, Walter M, Moseler M. Interactions of polymers with reduced graphene oxide: van der Waals binding energies of benzene on graphene with defects[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2014, 16(1): 33-37. |
| 20 | Yeh I C, Andzelm J W. Computational study of structural and energetic properties of ammonium perchlorate at interfaces[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(22): 12297-12304. |
| 21 | Chigo Anota E, Torres Soto A, Cocoletzi G H. Studies of graphene-chitosan interactions and analysis of the bioadsorption of glucose and cholesterol[J]. Applied Nanoscience, 2014, 4(8): 911-918. |
| 22 | Kresse G, Hafner J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for open-shell transition metals[J]. Physical Review B, Condensed Matter, 1993, 48(17): 13115-13118. |
| 23 | Yu H B, Zhao J H, Wu C Z, et al. Highly efficient Ir-CoO x hybrid nanostructures for the selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2021, 37(5): 1894-1901. |
| 24 | Vanderbilt D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism[J]. Physical Review B, Condensed Matter, 1990, 41(11): 7892-7895. |
| 25 | Sholl D S, Steckel J A. 密度泛函理论[M]. 李健,周勇,译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014. |
| Sholl D S, Steckel J A. Density Functional Theory[M].Li J, Zhou Y, trans. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2014. | |
| 26 | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wave function analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| 27 | Manzetti S, Lu T, Behzadi H, et al. Intriguing properties of unusual silicon nanocrystals[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(95): 78192-78208. |
| 28 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 29 | 姚维尚, 吴文辉, 贾展宁, 等. 硝胺推进剂的界面键合作用[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 1995, 15(6): 74-78. |
| Yao W S, Wu W H, Jia Z N, et al. Investigation on interfacial bonding in HMX-containing model propellant composite[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 1995, 15(6): 74-78. | |
| 30 | 吴文辉, 黎玉钦, 张聪, 等. 中性聚合物键合剂对硝胺推进剂相界面的作用[J]. 推进技术, 2001, 22(4): 337-340. |
| Wu W H, Li Y Q, Zhang C, et al. Interfacial reinforcement of neutral polymeric bonding agents (NPBA) in nitramine propellants[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2001, 22(4): 337-340. | |
| 31 | 虞振飞. 高能固体推进剂相关组分物理相容性的分子模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016. |
| Yu Z F. Investigation of physical compatibility of related components in novel high energy solid propellant by molecular simulation[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. | |
| 32 | 王瑞. 含能分子系统中的分子间氢键作用特性及振动能量转移过程理论研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. |
| Wang R. Theoretical studies on the intermolecular hydrogen bonding properties and vibrational energy transfer processes in energetic molecule systems[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020. | |
| 33 | 刘新国, 刘佩进, 强洪夫. 复合固体推进剂脱湿研究进展[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2018, 41(3): 313-318, 337. |
| Liu X G, Liu P J, Qiang H F. Recent advances on research of the dewetting in composite solid propellants[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2018, 41(3): 313-318, 337. | |
| 34 | 时文欣, 贾旗, 高浩, 等. 氧化石墨烯对天然橡胶性能的影响[J]. 弹性体, 2021, 31(5): 17-24. |
| Shi W X, Jia Q, Gao H, et al. Effects of graphene oxide on the properties of natural rubber [J]. China Elastomerics, 2021, 31(5): 17-24. | |
| 35 | 杨永岗, 陈成猛, 温月芳, 等. 氧化石墨烯及其与聚合物的复合[J]. 新型炭材料, 2008, 23(3): 193-200. |
| Yang Y G, Chen C M, Wen Y F, et al. Oxidized graphene and graphene based polymer composites[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2008, 23(3): 193-200. | |
| 36 | Giesbers A J M, Bouten P C P, Cillessen J F M, et al. Defects, a challenge for graphene in flexible electronics[J]. Solid State Communications, 2016, 229: 49-52. |
| 37 | 马丽娟, 韩婷, 高升启, 等. 单缺陷对Sc, Ti, V修饰石墨烯的结构及储氢性能的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(21): 218802. |
| Ma L J, Han T, Gao S Q, et al. Effect of monovacancy on stability and hydrogen storage property of Sc/Ti/V-decorated graphene[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(21): 218802. | |
| 38 | Ugeda M M, Fernández-Torre D, Brihuega I, et al. Point defects on graphene on metals[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 107(11): 116803. |
| 39 | Ugeda M M, Brihuega I, Hiebel F, et al. Electronic and structural characterization of divacancies in irradiated graphene[J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 85(12): 121402. |
| 40 | Liu X J, Zhang X, Bo M L, et al. Coordination-resolved electron spectrometrics[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(14): 6746-6810. |
| 41 | 郝良鹏, 柴颂刚, 曾耀德, 等. 一种精确测定二氧化硅表面羟基数量的新方法[J]. 广州化工, 2019, 47(4): 93-94, 121. |
| Hao L P, Chai S G, Zeng Y D, et al. A new method for accurate determination of OH groups density on silica surface[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(4): 93-94, 121. | |
| 42 | Jin J Q, Wang X M, Wick C D, et al. Silica surface states and their wetting characteristics[J]. Surface Innovations, 2020, 8(3): 145-157. |
| [1] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [2] | 傅予, 刘兴翀, 王瀚雨, 李海敏, 倪亚飞, 邹文静, 雷月, 彭永姗. F3EACl修饰层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能提升的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [3] | 刘远超, 蒋旭浩, 邵钶, 徐一帆, 钟建斌, 李耑. 几何尺寸及缺陷对石墨炔纳米带热输运特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [4] | 杜峰, 尹思琦, 罗辉, 邓文安, 李传, 黄振薇, 王文静. H2在Mo x S y 团簇上吸附解离的尺寸效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3895-3903. |
| [5] | 俞夏琪, 冯格, 赵金燕, 李嘉远, 邓声威, 郑靖楠, 李雯雯, 王亚秋, 沈榄, 刘旭, 徐威威, 王建国, 王式彬, 姚子豪, 毛成立. 基体(TDI-TMP-T313)与氧化剂(AP)相互作用的第一性原理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3511-3517. |
| [6] | 罗小松, 黄金保, 周梅, 牟鑫, 徐伟伟, 吴雷. 对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯二聚体水/醇/氨解机理的理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 4859-4871. |
| [7] | 龚翔, 李林森, 姜召. PdCo/SiO2双金属催化剂用于杂环储氢载体的高效脱氢[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4448-4460. |
| [8] | 朱先会, 王甫, 夏杰成, 袁金良. 功能型离子液体协同吸收NH3和CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4324-4334. |
| [9] | 马生贵, 田博文, 周雨薇, 陈琳, 江霞, 高涛. 氮掺杂Stone-Wales缺陷石墨烯吸附H2S的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4496-4503. |
| [10] | 张芳芳, 韩敏, 赵娟, 凌丽霞, 章日光, 王宝俊. 单空缺石墨烯负载的Pd单原子催化剂上NO还原的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1382-1391. |
| [11] | 唐伟强, 谢鹏, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 反应密度泛函理论的构建与初步应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 633-652. |
| [12] | 唐子龙,肖凡凡,尹玉华,李森雨,汪靖伦. 功能硅烷在有机-无机复合固态电解质中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5002-5015. |
| [13] | 葛冰青, 阴义轩, 王亚溪, 张宏伟, 袁珮. 溶剂对丁腈橡胶溶解、尺寸、结构和催化加氢的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 543-554. |
| [14] | 刘佳鑫, 徐宇, 花儿. 异辛基乙二胺-酰基丙氨酸型质子化离子液体的分子间氢键相互作用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 15-22. |
| [15] | 狄玲, 陈放, 付荣荣, 杨辰, 邢杨, 王晓宁. 富电子LMOF对有机农药的检测机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3830-3838. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号