化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (7): 3038-3050.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230354
收稿日期:2023-04-10
修回日期:2023-06-10
出版日期:2023-07-05
发布日期:2023-08-31
通讯作者:
邓文义
作者简介:屈园浩(1997—),男,硕士研究生,15503949225@163.com
基金资助:
Yuanhao QU( ), Wenyi DENG(
), Wenyi DENG( ), Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU
), Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU
Received:2023-04-10
Revised:2023-06-10
Online:2023-07-05
Published:2023-08-31
Contact:
Wenyi DENG
摘要:
以活性炭、石墨以及两者不同比例的混合物为添加剂,研究了不同配比添加剂对污泥电渗脱水性能以及滤液品质[总有机碳(TOC)含量、重金属浓度、有机物组成等]的影响机理。结果表明,活性炭与石墨都能够提升污泥的脱水性与导电性,其中相较于石墨,单独投加活性炭对泥饼的含水率降低最为明显,当投加量为5%污泥干重(DS)时,脱水效果最优,泥饼真实含水率由无投加时的46.0%(质量)降为42.2%(质量),污泥表观含水率降为41.0%(质量)。活性炭或石墨投加可显著降低阴极电渗滤液的TOC和重金属浓度,其中活性炭效果最优,石墨效果最弱。当活性炭投加量从0%DS增加至20%DS时,阴极滤液TOC含量从3740.4 mg/L降至2160.0 mg/L,而Cu、Mn、Cr、Ni、Cd、Zn、Hg和Pb等重金属元素浓度的降幅为57%~100%。研究成果将为含碳材料强化污泥电渗脱水提供基础数据支撑,并为污泥电渗脱水技术推广应用奠定理论基础。
中图分类号:
屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050.
Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050.
| 含水率/%(质量) | pH | 电导率/(μS/cm) | 灰分(干基)/%(质量) | 挥发分(干基)/%(质量) | 固定碳(干基)/%(质量) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80.0±0.5 | 7.2±0.1 | 1175±50 | 45.9±0.5 | 47.8±0.5 | 6.3±0.5 |
表1 污泥基本性质
Table 1 Basic properties of sludge
| 含水率/%(质量) | pH | 电导率/(μS/cm) | 灰分(干基)/%(质量) | 挥发分(干基)/%(质量) | 固定碳(干基)/%(质量) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80.0±0.5 | 7.2±0.1 | 1175±50 | 45.9±0.5 | 47.8±0.5 | 6.3±0.5 |
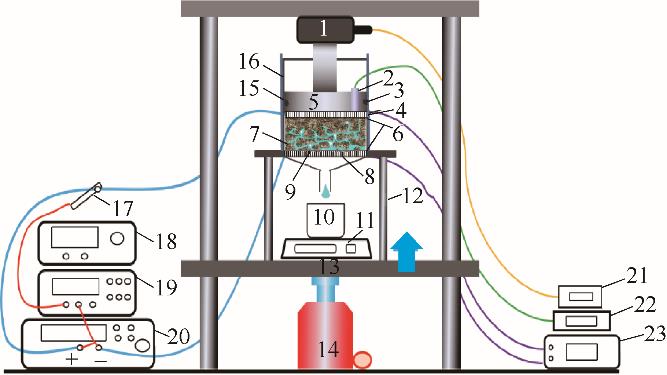
图1 电渗脱水装置1—压力传感器;2—热电偶;3—密封胶圈;4—钌铱钛阳极板;5—活塞;6—滤布;7—污泥样品;8—下过滤板;9—不锈钢阴极网;10—烧杯;11—电子天平;12—压片机支架;13—底座;14—千斤顶;15—绝缘套筒;16—金属套筒;17—电流探头;18—信号发生器;19—示波器;20—功率放大器;21—压力值数显表;22—温度数显;23—电压表
Fig.1 Electro-osmotic dewatering device1—pressure sensor; 2—thermocouple; 3—sealing apron; 4—ruthenium iridium titanium anode plate; 5—piston; 6—filter cloth; 7—sludge sample; 8—bottom filter plate; 9—stainless steel cathode mesh; 10—beaker; 11—electronic balance; 12—bracket; 13—base; 14—jack; 15—insulating sleeve; 16—metal sleeve; 17—current probe; 18—signal generator; 19—oscilloscope; 20—power amplifier; 21—digital display of pressure value; 22—digital display of temperature; 23—voltmeter
| 粒径/mm | 含水率/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| <0.056 | 41.8±0.2 |
| 0.056~0.1 | 41.0±0.2 |
| 0.1~0.335 | 41.3±0.2 |
| 0.335~0.5 | 42.0±0.2 |
| 0.5~0.8 | 42.5±0.2 |
| 0.8~1 | 42.1±0.2 |
表2 预实验结果
Table 2 The results of pre-experiments
| 粒径/mm | 含水率/%(质量) |
|---|---|
| <0.056 | 41.8±0.2 |
| 0.056~0.1 | 41.0±0.2 |
| 0.1~0.335 | 41.3±0.2 |
| 0.335~0.5 | 42.0±0.2 |
| 0.5~0.8 | 42.5±0.2 |
| 0.8~1 | 42.1±0.2 |
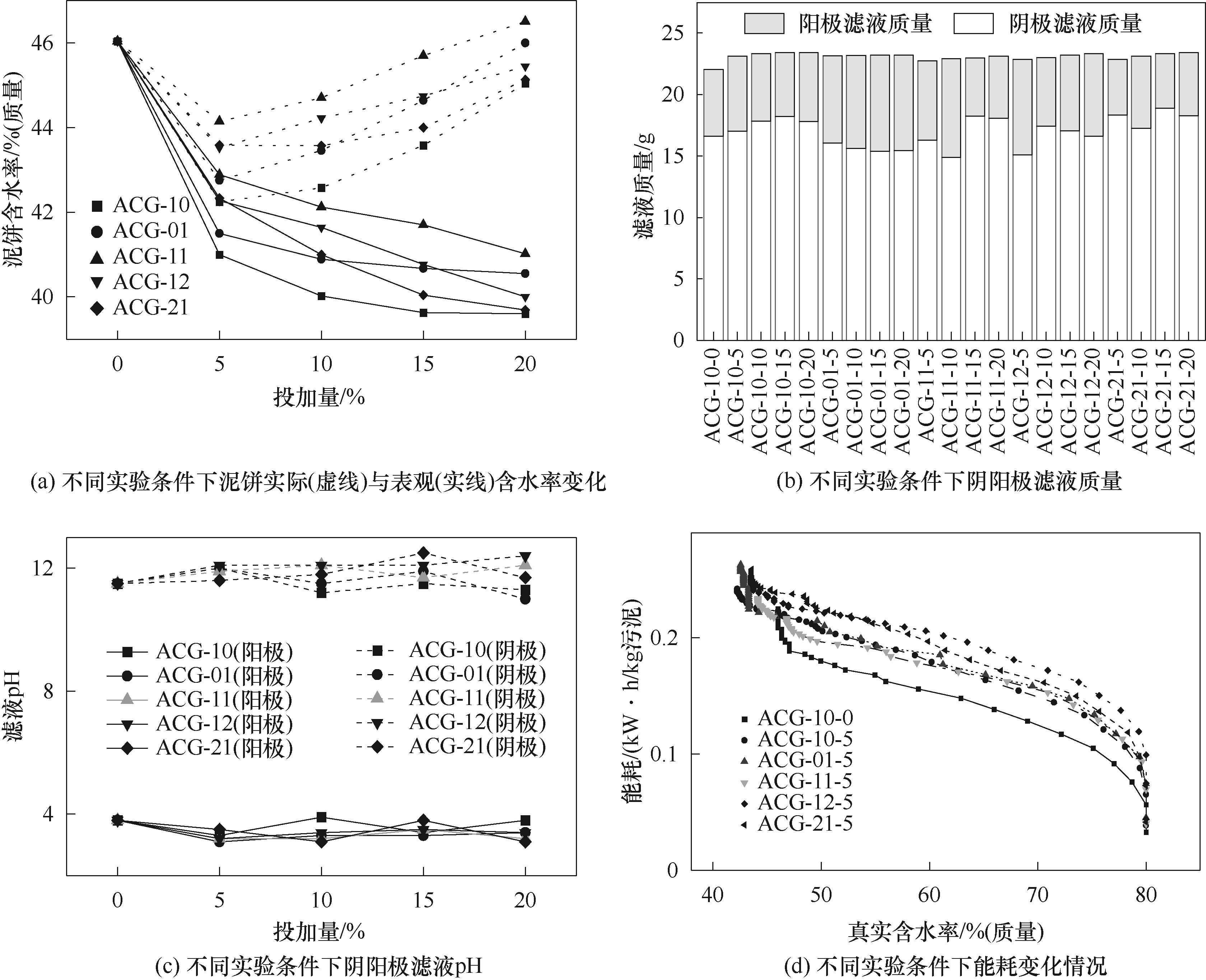
图2 电渗脱水污泥含水率(a)、总滤液质量(b)、pH(c)随添加剂投加量的变化以及能耗变化曲线(d)
Fig.2 Water content of sewage sludge (a), filtrate content of cathode and anode (b) and pH of filtrate (c) from electro-osmotic dewatering with different percentage of additives, and energy consumption change curve (d)
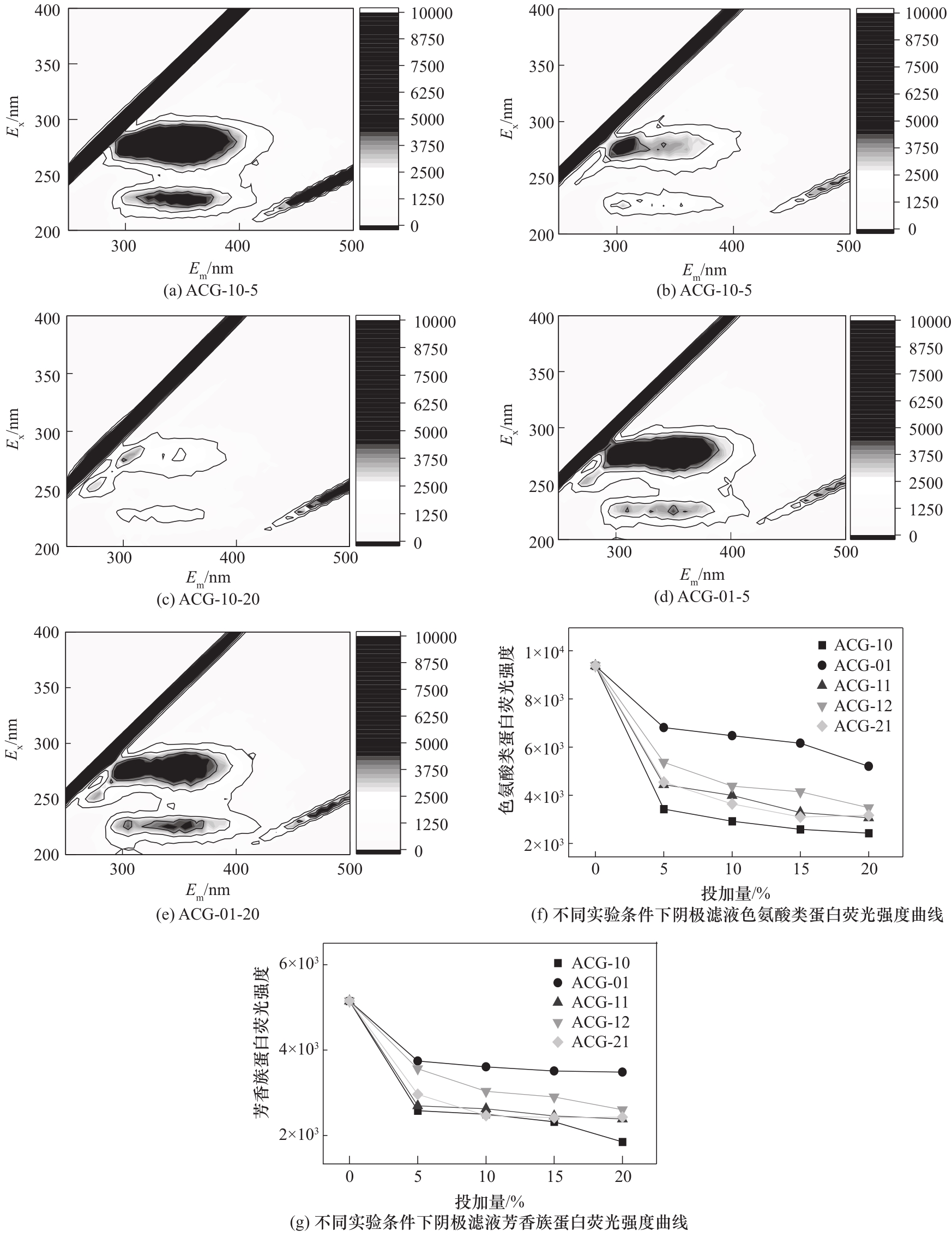
图8 阴极滤液3D-EEM谱图[(a)~(e)]和荧光强度随投加量的变化关系[(g),(f)]
Fig.8 3D-EEM spectra of cathodic filtrate [(a)—(e)], and variation of fluorescence intensity with additives [(g), (f)]
| 1 | 戴晓虎. 我国污泥处理处置现状及发展趋势[J]. 科学, 2020, 72(6): 30-34, 4. |
| Dai X H. Applications and perspectives of sludge treatment and disposal in China[J]. Science, 2020, 72(6): 30-34, 4. | |
| 2 | Kacprzak M, Neczaj E, Fijałkowski K, et al. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development [J]. Environmental Research, 2017, 156: 39-46. |
| 3 | Yang G, Zhang G M, Wang H C. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China[J]. Water Research, 2015, 78: 60-73. |
| 4 | Grobelak A, Czerwińska K, Murtaś A. General considerations on sludge disposal, industrial and municipal sludge[M]//Industrial and Municipal Sludge. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 135-153. |
| 5 | Qian X, Zhou X Q, Wu J D, et al. Electro-dewatering of sewage sludge: influence of combined action of constant current and constant voltage on performance and energy consumption[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 667: 751-760. |
| 6 | Mahmoud A, Olivier J, Vaxelaire J, et al. Electrical field: a historical review of its application and contributions in wastewater sludge dewatering[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(8): 2381-2407. |
| 7 | Rao B Q, Wang G Q, Xu P. Recent advances in sludge dewatering and drying technology[J]. Drying Technology, 2022, 40(15): 3049-3063. |
| 8 | Wei Y J, Zhou X Q, Zhou L, et al. Electro-dewatering of sewage sludge: effect of near-anode sludge modification with different dosages of calcium oxide[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 186: 109487. |
| 9 | 王晗. 电渗法在污泥脱水领域应用的影响因素[J]. 中国环保产业, 2022(11): 37-39, 42. |
| Wang H. Factors influencing the application of electroosmosis in the field of sludge dewatering[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2022 (11): 37-39, 42. | |
| 10 | 同帜, 王瑞露, 曹秉帝, 等. 炭材料调理改善活性污泥脱水性能的影响机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(7): 2094-2105. |
| Tong Z, Wang R L, Cao B D, et al. Mechanism of carbon conditioning for improving dewatering performance of activated sludge[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(7): 2094-2105. | |
| 11 | Mahmoud A, Hoadley A F A, Conrardy J B, et al. Influence of process operating parameters on dryness level and energy saving during wastewater sludge electro-dewatering[J]. Water Research, 2016, 103: 109-123. |
| 12 | Deng W Y, Lai Z C, Hu M H, et al. Effects of frequency and duty cycle of pulsating direct current on the electro-dewatering performance of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 243: 125372. |
| 13 | Liu C Y, Zhou X Q, Zhou L, et al. Enhancement of sludge electro-dewatering by anthracite powder modification[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 201: 111510. |
| 14 | Cao B D, Wang R L, Zhang W J, et al. Carbon-based materials reinforced waste activated sludge electro-dewatering for synchronous fuel treatment[J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 533-542. |
| 15 | Dong Y T, Yuan H P, Ge D D, et al. A novel conditioning approach for amelioration of sludge dewaterability using activated carbon strengthening electrochemical oxidation and realized mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2022, 220: 118704. |
| 16 | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,国家标准化管理委员会. 煤的工业分析方法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Proximate analysis of coal: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. | |
| 17 | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 纳米技术 碳纳米管粉体电阻率 四探针法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Nanotechnology—Resistivity of carbon nanotube powder—Four probe method: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. | |
| 18 | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 高绝缘电阻测量仪(高阻计)检定规程: [S]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 2004. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Verification Regulation of High Insulation Resistance Meters: [S]. Beijing: China Metrology Publishing House, 2004. | |
| 19 | 中华人民共和国建设部. 城市污水处理厂污泥检验方法: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. |
| Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic of China. Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006. | |
| 20 | Cao B D, Zhang W J, Du Y J, et al. Compartmentalization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) solubilization and cake microstructure in relation to wastewater sludge dewatering behavior assisted by horizontal electric field: effect of operating conditions[J]. Water Research, 2018, 130: 363-375. |
| 21 | Citeau M, Larue O, Vorobiev E. Influence of salt, pH and polyelectrolyte on the pressure electro-dewatering of sewage sludge[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(6): 2167-2180. |
| 22 | Clayton S A, Scholes O N, Hoadley A F A, et al. Dewatering of biomaterials by mechanical thermal expression[J]. Drying Technology, 2006, 24(7): 819-834. |
| 23 | Lv H, Liu D G, Zhang Y L, et al. Effects of temperature variation on wastewater sludge electro-dewatering[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 214: 873-880. |
| 24 | Weber K, Stahl W. Influence of an electric field on filtration in a filter press[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology: Industrial Chemistry-Plant Equipment-Process Engineering-Biotechnology, 2003, 26(1): 44-48. |
| 25 | Weber K, Stahl W. Improvement of filtration kinetics by pressure electrofiltration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2002, 26(1): 69-80. |
| 26 | Bergins C, Berger S, Strauß K. Dewatering of fossil fuels and suspensions of ultrafine particles by mechanical/thermal dewatering[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 1999, 22(11): 923-927. |
| 27 | Navab-Daneshmand T, Beton R, Hill R J, et al. Impact of Joule heating and pH on biosolids electro-dewatering[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5417-5424. |
| 28 | Hu S G, Hu J P, Sun Y F, et al. Simultaneous heavy metal removal and sludge deep dewatering with Fe (Ⅱ) assisted electrooxidation technology [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124072. |
| 29 | 王瑞露, 刘相汝, 曹秉帝, 等. 炭材料强化污泥电脱水效果及同步燃料化处理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(11): 4120-4129. |
| Wang R L, Liu X R, Cao B D, et al. Carbon material reinforced sludge electric-dewatering synchronous fuel treatment[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(11): 4120-4129. | |
| 30 | Rao B Q, Su J G, Xu J, et al. Coupling mechanism and parameter optimization of sewage sludge dewatering jointly assisted by electric field and mechanical pressure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152939. |
| 31 | Li Y L, Liu L, Li X R, et al. Influence of alternating electric field on deep dewatering of municipal sludge and changes of extracellular polymeric substance during dewatering[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 842: 156839. |
| 32 | 李亚林, 刘蕾, 张毅, 等. 电渗透/Fe-过硫酸盐氧化协同强化污泥深度脱水[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(9): 4013-4019. |
| Li Y L, Liu L, Zhang Y, et al. Coordination of electro-osmotic and Fe-persulfate oxidation process on sewage sludge deep-dewatering[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(9): 4013-4019. | |
| 33 | Barton W A, Miller S A, Veal C J. The electrodewatering of sewage sludges[J]. Drying Technology, 1999, 17(3): 498-522. |
| [1] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [3] | 吕龙义, 及文博, 韩沐达, 李伟光, 高文芳, 刘晓阳, 孙丽, 王鹏飞, 任芝军, 张光明. 铁基导电材料强化厌氧去除卤代有机污染物:研究进展及未来展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202. |
| [4] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [5] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [7] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [9] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [10] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [11] | 刘远超, 蒋旭浩, 邵钶, 徐一帆, 钟建斌, 李耑. 几何尺寸及缺陷对石墨炔纳米带热输运特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [12] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [13] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [14] | 郭旭, 张永政, 夏厚兵, 杨娜, 朱真珍, 齐晶瑶. 碳基材料电氧化去除水体污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [15] | 顾浩, 张福建, 刘珍, 周文轩, 张鹏, 张忠强. 力电耦合作用下多孔石墨烯膜时间维度的脱盐性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号