化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (2): 475-486.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190815
任六一1,2,3,4( ),赵颂1,2,3,4,王志1,2,3,4(
),赵颂1,2,3,4,王志1,2,3,4( ),燕方正1,2,3,4,刘莹莹1,2,3,4,韩向磊1,2,3,4,王纪孝1,2,3,4
),燕方正1,2,3,4,刘莹莹1,2,3,4,韩向磊1,2,3,4,王纪孝1,2,3,4
收稿日期:2019-07-15
修回日期:2019-10-08
出版日期:2020-02-05
发布日期:2020-02-05
通讯作者:
王志
作者简介:任六一(1995—),男,硕士研究生, 基金资助:
Liuyi REN1,2,3,4( ),Song ZHAO1,2,3,4,Zhi WANG1,2,3,4(
),Song ZHAO1,2,3,4,Zhi WANG1,2,3,4( ),Fangzheng YAN1,2,3,4,Yingying LIU1,2,3,4,Xianglei HAN1,2,3,4,Jixiao WANG1,2,3,4
),Fangzheng YAN1,2,3,4,Yingying LIU1,2,3,4,Xianglei HAN1,2,3,4,Jixiao WANG1,2,3,4
Received:2019-07-15
Revised:2019-10-08
Online:2020-02-05
Published:2020-02-05
Contact:
Zhi WANG
摘要:
聚酰胺反渗透膜具有选择透过性高、化学稳定性好等优点,在水处理领域应用广泛。但膜污染导致的通量下降、寿命降低等问题严重制约了其发展与应用,开发抗污染反渗透膜是缓解膜污染的重要手段。本文根据抗污染膜作用机理将抗污染反渗透膜分为抗黏附型、污染驱除型和杀菌型,综述了近年来相关方面的研究成果,并对合理组合多种机制制备抗污染反渗透膜的进展进行简要概括,最后对抗污染反渗透膜的发展前景进行了展望。
中图分类号:
任六一, 赵颂, 王志, 燕方正, 刘莹莹, 韩向磊, 王纪孝. 抗污染芳香聚酰胺反渗透膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 475-486.
Liuyi REN, Song ZHAO, Zhi WANG, Fangzheng YAN, Yingying LIU, Xianglei HAN, Jixiao WANG. Research progress of antifouling aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 475-486.
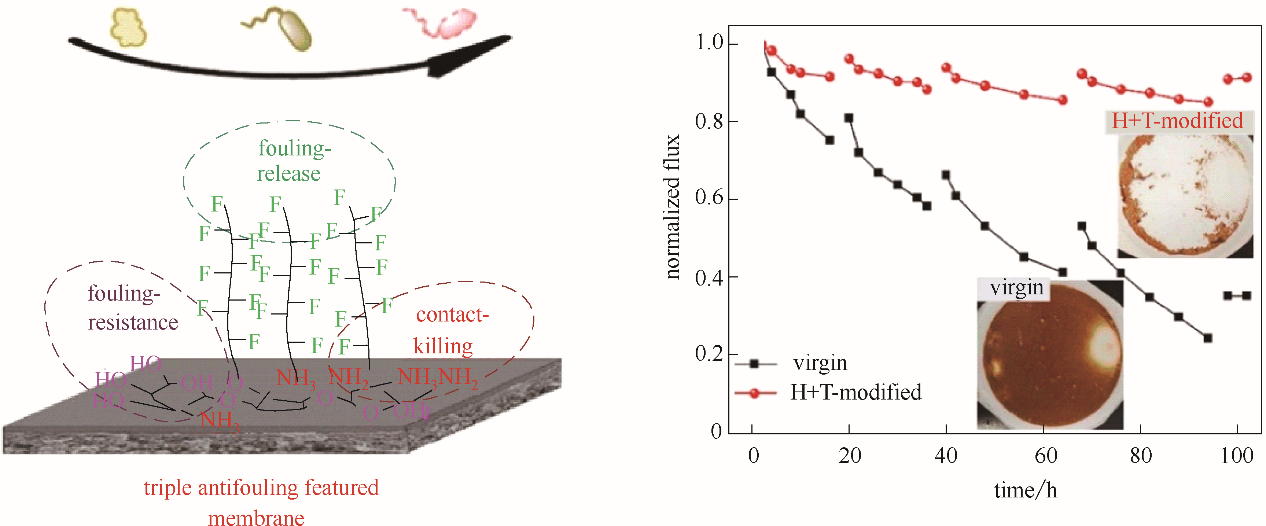
图7 三重抗污染功能反渗透膜及其抗污染性能 [ 82] (H + T-modified: HFBM和TOB改性的反渗透膜)
Fig.7 Triple antifouling features RO membrane and the corresponding antibiofouling property [ 82]
| 1 | Elimelech M, Phillip W A. The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment[J]. Science, 2011, 333( 6043): 712- 717. |
| 2 | Organization W H, Supply W U J W, Programme S M. Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water: 2015 Update and MDG Assessment[M]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015. |
| 3 | 徐建国, 尹华. 海水淡化反渗透膜技术的最新进展及其应用[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2014, 34( 2): 99- 105. |
| Xu J G, Yin H. Latest progress and applications of seawater RO membrane technology[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2014, 34( 2): 99- 105. | |
| 4 | Tong T Z, Wallace A F, Zhao S, et al. Mineral scaling in membrane desalination: mechanisms, mitigation strategies, and feasibility of scaling-resistant membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 579: 52- 69. |
| 5 | Li C Y, Guo X Y, Wang X, et al. Membrane fouling mitigation by coupling applied electric field in membrane system: configuration, mechanism and performance[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 287: 124- 134. |
| 6 | Matin A, Khan Z, Zaidi S M J, et al. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: phenomena and prevention[J]. Desalination, 2011, 281: 1- 16. |
| 7 | Wang K, Abdalla A A, Khaleel M A, et al. Mechanical properties of water desalination and wastewater treatment membranes[J]. Desalination, 2017, 401: 190- 205. |
| 8 | Kang G D, Cao Y M. Development of antifouling reverse osmosis membranes for water treatment: a review[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46( 3): 584- 600. |
| 9 | Jiang S, Li Y, Ladewig B P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 595: 567- 583. |
| 10 | Greenlee L F, Lawler D F, Freeman B D, et al. Reverse osmosis desalination: water sources, technology, and today s challenges[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43( 9): 2317- 2348. |
| 11 | Zhao X T, Zhang R N, Liu Y N, et al. Antifouling membrane surface construction: chemistry plays a critical role[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 551: 145- 171. |
| 12 | Wu J H, Wang Z, Yan W T, et al. Improving the hydrophilicity and fouling resistance of RO membranes by surface immobilization of PVP based on a metal-polyphenol precursor layer[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 496: 58- 69. |
| 13 | Wu J H, Wang Z, Wang Y, et al. Polyvinylamine-grafted polyamide reverse osmosis membrane with improved antifouling property[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 495: 1- 13. |
| 14 | Zhang Y, Wan Y, Pan G Y, et al. Surface modification of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane with sulfonated polyvinyl alcohol for antifouling[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 419: 177- 187. |
| 15 | Kang G D, Liu M, Lin B, et al. A novel method of surface modification on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane by grafting poly(ethylene glycol)[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48( 5): 1165- 1170. |
| 16 | Sagle A C, van Wagner E M, Ju H, et al. PEG-coated reverse osmosis membranes: desalination properties and fouling resistance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 340( 1/2): 92- 108. |
| 17 | Kang G D, Yu H J, Liu Z N, et al. Surface modification of a commercial thin film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by carbodiimide-induced grafting with poly(ethylene glycol) derivatives[J]. Desalination, 2011, 275( 1/ 2/ 3): 252- 259. |
| 18 | He M, Gao K, Zhou L, et al. Zwitterionic materials for antifouling membrane surface construction[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 40: 142- 152. |
| 19 | Wu J, Lin W, Wang Z, et al. Investigation of the hydration of nonfouling material poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28( 19): 7436- 7441. |
| 20 | Azari S, Zou L D. Using zwitterionic amino acid L-DOPA to modify the surface of thin film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes to increase their fouling resistance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 401: 68- 75. |
| 21 | Azari S, Zou L D. Fouling resistant zwitterionic surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes using amino acid L-cysteine[J]. Desalination, 2013, 324: 79- 86. |
| 22 | Yang Z, Saeki D, Matsuyama H. Zwitterionic polymer modification of polyamide reverse-osmosis membranes via surface amination and atom transfer radical polymerization for anti-biofouling [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 550: 332- 339. |
| 23 | Ma R, Ji Y L, Weng X D, et al. High-flux and fouling-resistant reverse osmosis membrane prepared with incorporating zwitterionic amine monomers via interfacial polymerization [J]. Desalination, 2016, 381: 100- 110. |
| 24 | Mccloskey B D, Park H B, Ju H, et al. Influence of polydopamine deposition conditions on pure water flux and foulant adhesion resistance of reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and microfiltration membranes[J]. Polymer, 2010, 51( 15): 3472- 3485. |
| 25 | Li H, Peng L, Luo Y B, et al. Enhancement in membrane performances of a commercial polyamide reverse osmosis membrane via surface coating of polydopamine followed by the grafting of polyethylenimine [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5( 119): 98566- 98575. |
| 26 | Baek Y, Freeman B D, Zydney A L, et al. A facile surface modification for antifouling reverse osmosis membranes using polydopamine under UV irradiation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56( 19): 5756- 5760. |
| 27 | Yu S C, Yao G H, Dong B Y, et al. Improving fouling resistance of thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by coating natural hydrophilic polymer sericin[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2013, 118: 285- 293. |
| 28 | Zhang F, Wu Y P, Li W X, et al. Depositing lignin on membrane surfaces for simultaneously upgraded reverse osmosis performances: an upscalable route[J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63( 6): 2221- 2231. |
| 29 | Choi W, Choi J, Bang J, et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide nanosheets on polyamide membranes for durable reverse-osmosis applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2013, 5( 23): 12510- 12519. |
| 30 | Zhao H Y, Qiu S, Wu L G, et al. Improving the performance of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by incorporation of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 450: 249- 256. |
| 31 | 邬军辉. 抗污染反渗透膜及其中试生产线研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2015. |
| Wu J H. Study of antifouling reverse osmosis membranes and their pilot-scale production line[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2015 | |
| 32 | Koo J Y, Hong S P, Lee J H, et al. Selective membrane having a high fouling resistance: US7913857 B2[P]. 2011-03-29. |
| 33 | de Vos W M, Leermakers F A M, Lindhoud S, et al. Modeling the structure and antifouling properties of a polymer brush of grafted comb-polymers[J]. Macromolecules, 2011, 44( 7): 2334- 2342. |
| 34 | Sarkar A, Carver P I, Zhang T, et al. Dendrimer-based coatings for surface modification of polyamide reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 349( 1/2): 421- 428. |
| 35 | Nikolaeva D, Langner C, Ghanem A, et al. Hydrogel surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 476: 264- 276. |
| 36 | Chen L Y, Zhang P, Gai J G. Dendritic molecules give excellent long-lasting desalination fouling resistance to reverse osmosis membrane by generating an amine-rich layer[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019, 136( 17): 47368. |
| 37 | Yang Z, Saeki D, Wu H C, et al. Effect of polymer structure modified on RO membrane surfaces via surface-initiated ATRP on dynamic biofouling behavior [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 582: 111- 119. |
| 38 | Chen W, Su Y, Peng J, et al. Engineering a robust, versatile amphiphilic membrane surface through forced surface segregation for ultralow flux-decline[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21( 1): 191- 198. |
| 39 | Zhao X T, Su Y L, Dai H, et al. Coordination-enabled synergistic surface segregation for fabrication of multi-defense mechanism membranes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3( 7): 3325- 3331. |
| 40 | Galli G, Martinelli E. Amphiphilic polymer platforms: surface engineering of films for marine antibiofouling[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2017, 38( 8): 1600704. |
| 41 | Choi H, Park J, Tak T, et al. Surface modification of seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) membrane using methyl methacrylate-hydroxy poly(oxyethylene) methacrylate (MMA-HPOEM) comb-polymer and its performance[J]. Desalination, 2012, 291: 1- 7. |
| 42 | Matin A, Shafi H, Wang M, et al. Reverse osmosis membranes surface-modified using an initiated chemical vapor deposition technique show resistance to alginate fouling under cross-flow conditions: filtration & subsequent characterization[J]. Desalination, 2016, 379: 108- 117. |
| 43 | Dutta K, De S. Smart responsive materials for water purification: an overview[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5( 42): 22095- 22112. |
| 44 | You M, Wang P, Xu M L, et al. Fouling resistance and cleaning efficiency of stimuli-responsive reverse osmosis (RO) membranes[J]. Polymer, 2016, 103: 457- 467. |
| 45 | Wu D H, Liu X S, Yu S C, et al. Modification of aromatic polyamide thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes by surface coating of thermo-responsive copolymers P(NIPAM- co-Am(Ⅰ): Preparation and characterization [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 352( 1/2): 76- 85. |
| 46 | Yu S C, Liu X S, Liu J Q, et al. Surface modification of thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes with thermo-responsive polymer (TRP) for improved fouling resistance and cleaning efficiency[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 76( 3): 283- 291. |
| 47 | Meng J Q, Cao Z, Ni L, et al. A novel salt-responsive TFC RO membrane having superior antifouling and easy-cleaning properties[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 461: 123- 129. |
| 48 | Slavin Y N, Asnis J, Hafeli U O, et al. Metal nanoparticles: understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2017, 15( 1): 65. |
| 49 | Kim S H, Kwak S Y, Sohn B H, et al. Design of TiO 2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane as an approach to solve biofouling problem [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2003, 211( 1): 157- 165. |
| 50 | Yang H L, Lin J C, Huang C. Application of nanosilver surface modification to RO membrane and spacer for mitigating biofouling in seawater desalination[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43( 15): 3777- 3786. |
| 51 | Ben-Sasson M, Lu X, Bar-Zeev E, et al. In situ formation of silver nanoparticles on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes for biofouling mitigation [J]. Water Research, 2014, 62: 260- 270. |
| 52 | Ben-Sasson M, Lu X L, Nejati S, et al. In situ surface functionalization of reverse osmosis membranes with biocidal copper nanoparticles [J]. Desalination, 2016, 388: 1- 8. |
| 53 | Dong C X, Wang Z, Wu J H, et al. A green strategy to immobilize silver nanoparticles onto reverse osmosis membrane for enhanced anti-biofouling property[J]. Desalination, 2017, 401: 32- 41. |
| 54 | Yin J, Yang Y, Hu Z Q, et al. Attachment of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) onto thin-film composite (TFC) membranes through covalent bonding to reduce membrane biofouling[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 441: 73- 82. |
| 55 | Park S H, Ko Y S, Park S J, et al. Immobilization of silver nanoparticle-decorated silica particles on polyamide thin film composite membranes for antibacterial properties[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 499: 80- 91. |
| 56 | 江山, 王立, 俞豪杰, 等. 新型有机高分子抗菌剂[J]. 高分子通报, 2002, ( 6): 57- 62. |
| Jiang S, Wang L, Yu H J, et al. Novel organic polymeric biocides[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2002, ( 6): 57- 62. | |
| 57 | Yudovin-Farber I, Golenser J, Beyth N, et al. Quaternary ammonium polyethyleneimine: antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2010, 2010: 1- 11. |
| 58 | Hibbs M R, Mcgrath L K, Kang S, et al. Designing a biocidal reverse osmosis membrane coating: synthesis and biofouling properties[J]. Desalination, 2016, 380: 52- 59. |
| 59 | Dong A, Wang Y J, Gao Y, et al. Chemical insights into antibacterial N-halamines [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117( 6): 4806- 4862. |
| 60 | Wei X Y, Wang Z, Chen J, et al. A novel method of surface modification on thin-film-composite reverse osmosis membrane by grafting hydantoin derivative[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 346( 1): 152- 162. |
| 61 | Wei X Y, Wang Z, Zhang Z, et al. Surface modification of commercial aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes by graft polymerization of 3-allyl-5,5-dimethylhydantoin[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 351( 1/2): 222- 233. |
| 62 | Zhang Z, Wang Z, Wang J, et al. Enhancing chlorine resistances and anti-biofouling properties of commercial aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes by grafting 3-allyl-5,5-dimethylhydantoin and N,N′-methylenebis(acrylamide) [J]. Desalination, 2013, 309: 187- 196. |
| 63 | Xu J, Wang Z, Yu L L, et al. A novel reverse osmosis membrane with regenerable anti-biofouling and chlorine resistant properties[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 435: 80- 91. |
| 64 | Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang J X. Lab-scale and pilot-scale fabrication of amine-functional reverse osmosis membrane with improved chlorine resistance and antimicrobial property[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 554: 221- 231. |
| 65 | Salgueiro A M, Santos M D, Saraiva J A, et al. Ultra-high pressure modified cellulosic fibres with antimicrobial properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017, 175: 303- 310. |
| 66 | 周艺璇, 王志, 董晨曦, 等. 双胍基化聚乙烯胺改性制备抗生物污染反渗透膜[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69( 2): 858- 865. |
| Zhou Y X, Wang Z, Dong C X, et al. Biguanidine functionalized polyvinylamine modified reverse osmosis membrane with improved anti-bacterial property[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69( 2): 858- 865. | |
| 67 | Wang H H, Zhou Y X, Wang Y, et al. Biguanidine functional chitooligosaccharide modified reverse osmosis membrane with improved anti-biofouling property[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8( 73): 41938- 41949. |
| 68 | Glinel K, Thebault P, Humblot V, et al. Antibacterial surfaces developed from bio-inspired approaches[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8( 5): 1670- 1684. |
| 69 | Saeki D, Nagao S, Sawada I, et al. Development of antibacterial polyamide reverse osmosis membrane modified with a covalently immobilized enzyme[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 428: 403- 409. |
| 70 | Bodner E J, Kandiyote N S, Lutskiy M Y, et al. Attachment of antimicrobial peptides to reverse osmosis membranes by Cu (I)-catalyzed 1, 3-dipolar alkyne–azide cycloaddition[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6( 94): 91815- 91823. |
| 71 | Kandiyote N S, Mohanraj G, Mao C, et al. Synergy on surfaces: anti-biofouling interfaces using surface-attached antimicrobial peptides PGLa and Magainin-2[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34( 37): 11147- 11155. |
| 72 | Habimana O, Semião A J C, Casey E. The role of cell-surface interactions in bacterial initial adhesion and consequent biofilm formation on nanofiltration/reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 454: 82- 96. |
| 73 | Nikkola J, Liu X, Li Y, et al. Surface modification of thin film composite RO membrane for enhanced anti-biofouling performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 444: 192- 200. |
| 74 | Wang J, Wang Z, Wang J X, et al. Improving the water flux and bio-fouling resistance of reverse osmosis (RO) membrane through surface modification by zwitterionic polymer[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 493: 188- 199. |
| 75 | Liu C, Faria A F, Ma J, et al. Mitigation of biofilm development on thin-film composite membranes functionalized with zwitterionic polymers and silver nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51( 1): 182- 191. |
| 76 | Ye G, Lee J, Perreault F, et al. Controlled architecture of dual-functional block copolymer brushes on thin-film composite membranes for integrated “defending” and “attacking” strategies against biofouling[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2015, 7( 41): 23069- 23079. |
| 77 | Perreault F, De Faria A F, Nejati S, et al. Antimicrobial properties of graphene oxide nanosheets: why size matters[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9( 7): 7226- 7236. |
| 78 | Huang X, Marsh K L, Mcverry B T, et al. Low-fouling antibacterial reverse osmosis membranes via surface grafting of graphene oxide [J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2016, 8( 23): 14334- 14338. |
| 79 | Wang Y, Wang Z, Han X L, et al. Improved flux and anti-biofouling performances of reverse osmosis membrane via surface layer-by-layer assembly [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 539: 403- 411. |
| 80 | Pan Y, Ma L J, Lin S, et al. One-step bimodel grafting via a multicomponent reaction toward antifouling and antibacterial TFC RO membranes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4( 41): 15945- 15960. |
| 81 | Rahaman M S, Therien-Aubin H, Ben-Sasson M, et al. Control of biofouling on reverse osmosis polyamide membranes modified with biocidal nanoparticles and antifouling polymer brushes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2( 12): 1724- 1732. |
| 82 | Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang J X, et al. Triple antifouling strategies for reverse osmosis membrane biofouling control[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549: 495- 506. |
| [1] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 靳龙, 王宇涛, 黄睿宁. 超声波激励下铝板表面液滴群输运特性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 104-112. |
| [2] | 邵苛苛, 宋孟杰, 江正勇, 张旋, 张龙, 高润淼, 甄泽康. 水平方向上冰中受陷气泡形成和分布实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 161-164. |
| [3] | 吴延鹏, 李晓宇, 钟乔洋. 静电纺丝纳米纤维双疏膜油性细颗粒物过滤性能实验分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 259-264. |
| [4] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [5] | 胡建波, 刘洪超, 胡齐, 黄美英, 宋先雨, 赵双良. 有机笼跨细胞膜易位行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [6] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [7] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [8] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [9] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [10] | 陈天华, 刘兆轩, 韩群, 张程宾, 李文明. 喷雾冷却换热强化研究进展及影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3149-3170. |
| [11] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [12] | 张佳怡, 何佳莉, 谢江鹏, 王健, 赵鹬, 张栋强. 渗透汽化技术用于锂电池生产中N-甲基吡咯烷酮回收的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [13] | 张贲, 王松柏, 魏子亚, 郝婷婷, 马学虎, 温荣福. 超亲水多孔金属结构驱动的毛细液膜冷凝及传热强化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2824-2835. |
| [14] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [15] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号