CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2929-2938.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241446
• Surface and interface engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pinxian LI( ), Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO(
), Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO( ), Boyao WEN(
), Boyao WEN( ), Bofeng BAI
), Bofeng BAI
Received:2024-12-13
Revised:2025-01-17
Online:2025-07-09
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Zhengyuan LUO, Boyao WEN
通讯作者:
骆政园,温伯尧
作者简介:李品贤(2002—),男,硕士研究生,xian.2002@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Pinxian LI, Feng GUO, Zhengyuan LUO, Boyao WEN, Bofeng BAI. Regulation of nanoparticle adsorption interface on droplet migration and blockage in micropore throat[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2929-2938.
李品贤, 郭峰, 骆政园, 温伯尧, 白博峰. 纳米颗粒吸附界面对微孔喉中液滴运移及堵塞的调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2929-2938.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
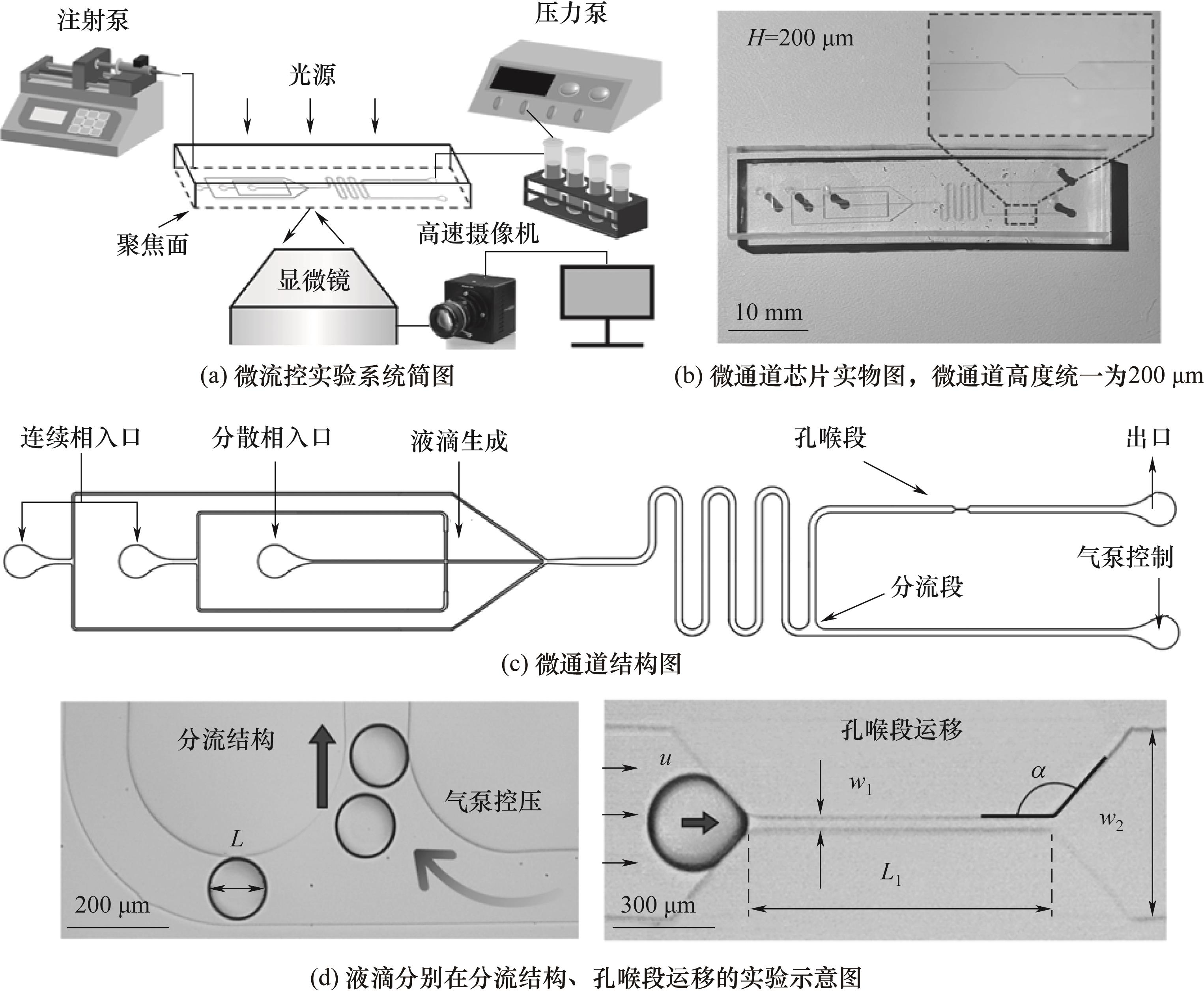
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the experimental system, microchannel structure, and the limited blockage of droplets at the pore-throat section of the microchannel
| 试剂组别 | COOH-PS(质量分数)/% | NH2-PDMS-NH2(质量分数)/% | γ/(mN/m) | ρ/(g/cm3) | μ/(mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯水纯油 | 0 | 0 | 25.2±0.6 | — | — |
| 仅添加纳米颗粒 | 0.5 | 0 | 24.7±0.4 | — | — |
| 纳米颗粒表面活性剂 | 0.001 | 1 | 12.0±0.7 | 0.998(W)/0.963(O) | 1(W)/10O) |
| 0.005 | 1 | 10.3±0.7 | — | — | |
| 0.05 | 1 | 6.4±0.8 | — | — |
Table 1 The relative parameters for three different fluid systems
| 试剂组别 | COOH-PS(质量分数)/% | NH2-PDMS-NH2(质量分数)/% | γ/(mN/m) | ρ/(g/cm3) | μ/(mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯水纯油 | 0 | 0 | 25.2±0.6 | — | — |
| 仅添加纳米颗粒 | 0.5 | 0 | 24.7±0.4 | — | — |
| 纳米颗粒表面活性剂 | 0.001 | 1 | 12.0±0.7 | 0.998(W)/0.963(O) | 1(W)/10O) |
| 0.005 | 1 | 10.3±0.7 | — | — | |
| 0.05 | 1 | 6.4±0.8 | — | — |
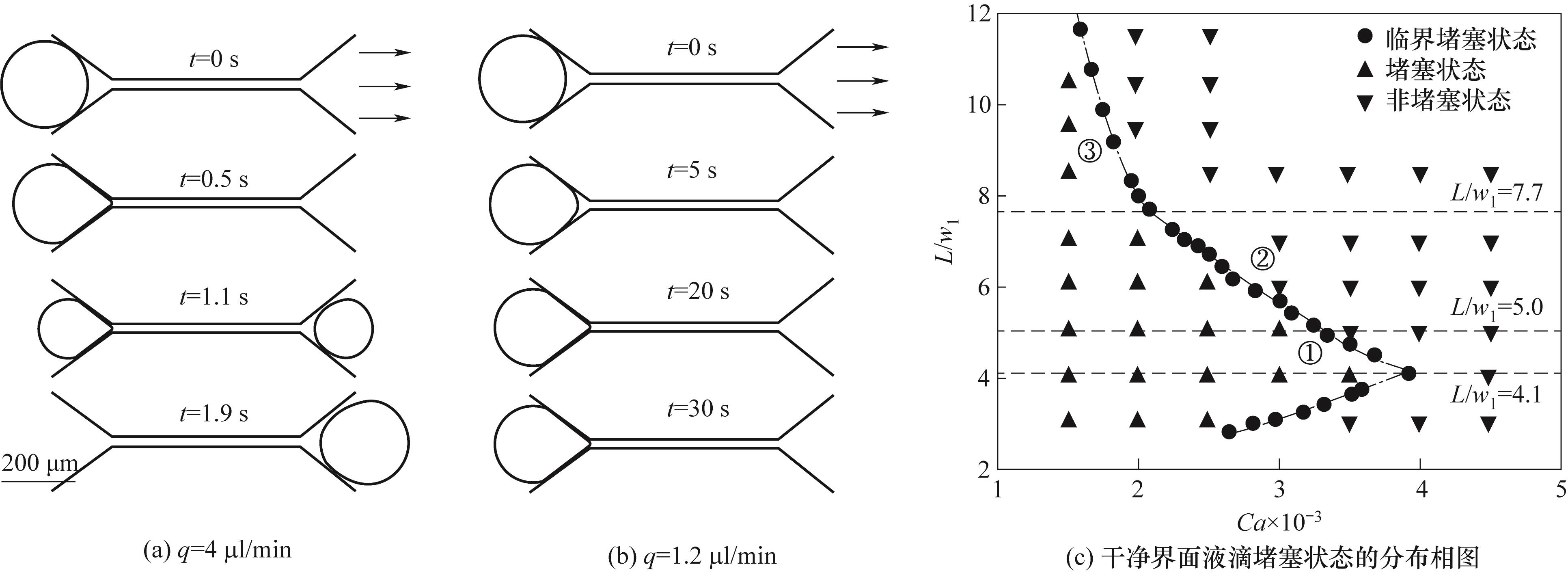
Fig.2 Time evolution of the same size droplet (L/w1 = 6.5) passing through the pore-throat structure under different flow rates (a)、(b); the distribution phase diagram of the blocked state of the clean interface droplet (c) (The dotted line represents the theoretical prediction of the blocked state and the non-blocked state)
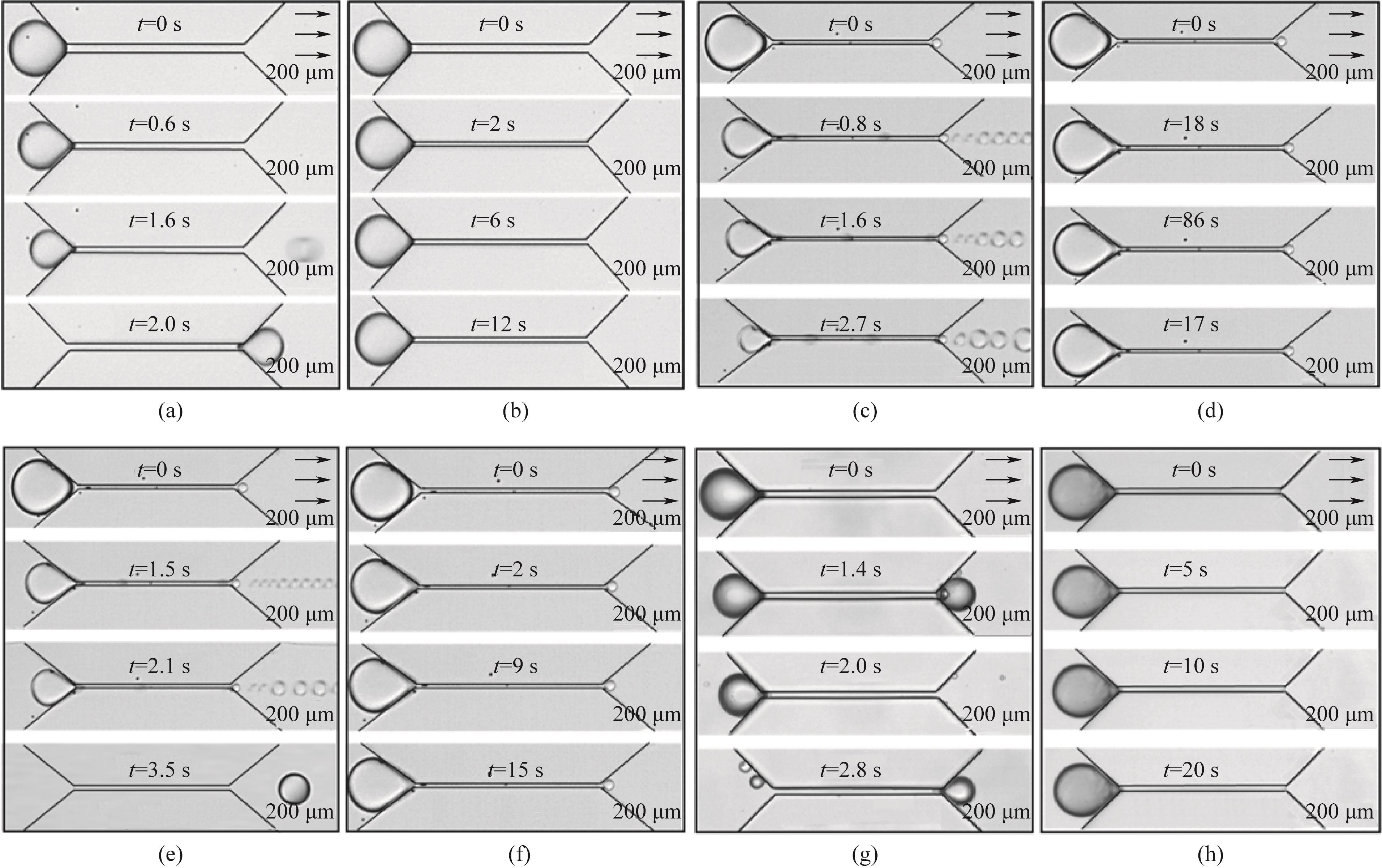
Fig.4 Time evolution of migration droplets (the same size L/w1 = 3.5) passing through the micropore throat under the action of different reagents. (a) Pure liquid group, flow rate q = 4.0 μl·min-1; (b) Pure liquid group, flow rate q = 2.9 μl·min-1; (c) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, and the flow rate q = 3.5 μl·min-1; (d) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, and the flow rate q = 3.1 μl·min-1; (e) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate was 1.6 μl·min-1; (f) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 0.9 μl·min-1; (g) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.5%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 1.5 μl·min-1; (h) The concentration of nanoparticles was 0.005%, the concentration of polymer surfactant was 1%, and the flow rate q = 1.0 μl·min-1
| [1] | Du S H, Shi Y M. Concise extraction and characterization of the pore-throat network in unconventional hydrocarbon reservoirs: a new perspective[J]. Petroleum Science, 2024, 21(3): 1474-1487. |
| [2] | Singh K, Jung M, Brinkmann M, et al. Capillary-dominated fluid displacement in porous media[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 51: 429-449. |
| [3] | 罗莉涛, 廖广志, 刘卫东, 等. Marangoni对流启动残余油微观机理[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9): 1127-1134. |
| Luo L T, Liao G Z, Liu W D, et al. Micromechanism of residual oil mobilization by Marangoni convection[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1127-1134. | |
| [4] | Lai J, Wang G W, Wang Z Y, et al. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 436-457. |
| [5] | 吴飞鹏, 李娜, 杨维, 等. 水力脉动波驱动微观剩余油实验与机理分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(6): 1217-1226. |
| Wu F P, Li N, Yang W, et al. Experimental characterization and mechanism analysis of hydraulic pulsation waves driving microscopic residual oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(6): 1217-1226. | |
| [6] | Liu Z X, Liang Y, Wang Q, et al. Status and progress of worldwide EOR field applications[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 193: 107449. |
| [7] | Habib S H, Yunus R, Zakaria R, et al. Chemical enhanced oil recovery: synergetic mechanism of alkali, surfactant and polymer with overview of methyl ester sulfonate as a green alternative for EOR surfactant[J]. Fuel, 2024, 363: 130957. |
| [8] | Mir H, Siavashi M. Whole-time scenario optimization of steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) with temperature, pressure, and rate control using an efficient hybrid optimization technique[J]. Energy, 2022, 239: 122149. |
| [9] | Tan Y S, Li Q, Xu L, et al. A critical review of carbon dioxide enhanced oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Fuel, 2022, 328: 125256. |
| [10] | Shi N, Mohibullah M, Easley C J. Active flow control and dynamic analysis in droplet microfluidics[J]. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 14(1): 133-153. |
| [11] | Padmanabhan S, Misteli T, DeVoe D L. Controlled droplet discretization and manipulation using membrane displacement traps[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(21): 3717-3724. |
| [12] | Rambach R W, Biswas P, Yadav A, et al. Fast selective trapping and release of picoliter droplets in a 3D microfluidic PDMS multi-trap system with bubbles[J]. The Analyst, 2018, 143(4): 843-849. |
| [13] | Carreras M P, Wang S H. A multifunctional microfluidic platform for generation, trapping and release of droplets in a double laminar flow[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 251: 106-111. |
| [14] | Courtney M, Chen X M, Chan S, et al. Droplet microfluidic system with on-demand trapping and releasing of droplet for drug screening applications[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(1): 910-915. |
| [15] | Zhang Z F, Drapaca C, Chen X L, et al. Droplet squeezing through a narrow constriction: minimum impulse and critical velocity[J]. 2017, 29(7): 072102. |
| [16] | Liang M C, Yang S S, Miao T J, et al. Minimum applied pressure for a drop through an abruptly constricted capillary[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2015, 19(1): 1-8. |
| [17] | Zhang Z F, Drapaca C, Gritsenko D, et al. Pressure of a viscous droplet squeezing through a short circular constriction: an analytical model[J]. 2018, 30(10): 102004. |
| [18] | He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F. Release of a trapped droplet in a single micro pore throat[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 554: 1-8. |
| [19] | Imani G, Zhang L, Xu C, et al. Finite droplets vs long droplets: discrepancy in release conditions in a microscopic constricted channel[J]. 2023, 35(3): 032101. |
| [20] | Wen B Y, Sun C Z, Bai B F. Nanoparticle-induced ion-sensitive reduction in decane-water interfacial tension[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(35): 22796-22804. |
| [21] | 赵赫, 费滢洁, 朱春英, 等. 高黏体系中纳米颗粒稳定气泡的形变及破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| Zhao H, Fei Y J, Zhu C Y, et al. Deformation and breakup behavior of nanoparticle-stabilized bubbles in high-viscosity systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. | |
| [22] | Xu K, Zhu P X, Huh C, et al. Microfluidic investigation of nanoparticles' role in mobilizing trapped oil droplets in porous media[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(51): 13673-13679. |
| [23] | Frijters S, Günther F, Harting J. Effects of nanoparticles and surfactant on droplets in shear flow[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(24): 6542-6556. |
| [24] | Cui M M, Emrick T, Russell T P. Stabilizing liquid drops in nonequilibrium shapes by the interfacial jamming of nanoparticles[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6157): 460-463. |
| [25] | Toor A, Helms B A, Russell T P. Effect of nanoparticle surfactants on the breakup of free-falling water jets during continuous processing of reconfigurable structured liquid droplets[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(5): 3119-3125. |
| [26] | Toor A, Lamb S, Helms B A, et al. Reconfigurable microfluidic droplets stabilized by nanoparticle surfactants[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(3): 2365-2372. |
| [27] | Chai Y, Lukito A, Jiang Y, et al. Fine-tuning nanoparticle packing at water-oil interfaces using ionic strength[J]. Nano letters, 2017, 17(10): 6453-6457. |
| [28] | Subramanian R S. The Stokes force on a droplet in an unbounded fluid medium due to capillary effects[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1985, 153: 389-400. |
| [29] | He L, Luo Z Y, Bai B F. Breakup of pancake droplets flowing through a microfluidic constriction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 220: 115649. |
| [30] | Shi S W, Russell T P. Nanoparticle assembly at liquid–liquid interfaces: from the nanoscale to mesoscale[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(44): 1800714. |
| [31] | Wang B B, Yin B Q, Zhang Z, et al. The assembly and jamming of nanoparticle surfactants at liquid-liquid interfaces[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(10): e202114936. |
| [32] | Luo Y Z, Yang Y, Wang Y K, et al. Reconfigurable liquids constructed by pillar [6] arene-based nanoparticle surfactants[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(33): e202207199. |
| [1] | Juhui CHEN, Ke CHEN, Dan LI, Tianyi YANG, Michael ZHURAVKOV, Siarhel LAPATSIN, Wenrui JIANG. Fluidization research on the FCC-assisted nanoparticle hybrid system based on the multicomponent DQMOM model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2616-2625. |
| [2] | Ben’an CAI, Jianxin ZHANG, Chengjun LONG, Qiaochen DU, Xunjian CHE, Yiying ZHANG, Weihua CAI. Spray flash evaporation preparation of micro/nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1334-1345. |
| [3] | Wenbao LI, Jinpeng HU, Miao DU, Pengju PAN, Guorong SHAN. High strength and toughness P(SBMA-co-AAc)/SiO2 composite hydrogel marine antifouling and drag-reducing coating [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 787-796. |
| [4] | Siwen ZHANG, Haiming GU, Shanhui ZHAO. Molecular mechanism study on chemical looping gasification of cellulose over iron oxide nanocluster [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 363-373. |
| [5] | Lü LIU, Jieru LIU, Liangliang FAN, Liang ZHAO. Study on passive microfluidic method for particle separation based on laminar effect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 67-75. |
| [6] | Nana SUN, Hongmei DONG, Wenhao GUO, Jian LIU, Jianbo HU, Shuang JIN. Rheological property influencing factors and a pressure drop prediction model for pipeline transportation in thick oil O/W emulsions stabilized by modified magnetic nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 143-157. |
| [7] | He ZHAO, Yingjie FEI, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Youguang MA. Deformation and breakup behavior of nanoparticle-stabilized bubbles in high-viscosity systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| [8] | Wenyan ZHANG, Hao LIU, Weilong SONG, Pin ZHAO, Xinhua WANG. Construction and performance evaluation of TFN-FO membranes incorporated with UiO-66 nanoparticles of different sizes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1920-1928. |
| [9] | Mengqi LIU, Kai WANG, Guangsheng LUO. Fundamental research on microdispersion based on artificial intelligence [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1096-1104. |
| [10] | Zhouyang SHEN, Kang XUE, Qing LIU, Chengxiang SHI, Jijun ZOU, Xiangwen ZHANG, Lun PAN. Research progress on endothermic nanofluid fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1167-1182. |
| [11] | Xiaoying JI, Yuan ZHENG, Xiaopeng LI, Zhen YANG, Wei ZHANG, Shirui QIU, Qianying ZHANG, Canghai LUO, Dongpeng SUN, Dong CHEN, Dongliang LI. Controlled preparation of droplets, particles and capsules by microfluidics and their applications [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1455-1468. |
| [12] | Zhanzhu CHEN, Jinhua YE, Zhibin WANG, Zhi YANG, Lisi JIA, Ying CHEN. Efficient generation of droplets through three-dimensional fractal integrated coaxial flow channels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4442-4452. |
| [13] | Xiaojie JU, Mingwei HE, Youqiang XIA, Wei WANG, Liangyin CHU. Research progress on controllable fabrication of anisotropic microfibers by microfluidics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 3923-3934. |
| [14] | Yewei DING, Wenbo KANG, Yutong SONG, Qinxi FAN, Yuanhui JI. Mechanism and screening of indomethacin self-assembled nanomedical drugs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4141-4151. |
| [15] | Dewang ZHANG, Qiankun ZHAO, Xiaoni GUO, Chaoqun YAO, Guangwen CHEN. Flow and mass transfer characteristics of Newtonian/non-Newtonian liquid-liquid flow in a microreactor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4162-4169. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||