化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (9): 4594-4606.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210186
张文龙1,2( ),侯燕1,靳海波1,2(
),侯燕1,靳海波1,2( ),马磊1,2,何广湘1,2,杨索和1,2,郭晓燕1,2,张荣月1,2
),马磊1,2,何广湘1,2,杨索和1,2,郭晓燕1,2,张荣月1,2
收稿日期:2021-01-29
修回日期:2021-05-31
出版日期:2021-09-05
发布日期:2021-09-05
通讯作者:
靳海波
作者简介:张文龙(1995—),男,硕士研究生,
Wenlong ZHANG1,2( ),Yan HOU1,Haibo JIN1,2(
),Yan HOU1,Haibo JIN1,2( ),Lei MA1,2,Guangxiang HE1,2,Suohe YANG1,2,Xiaoyan GUO1,2,Rongyue ZHANG1,2
),Lei MA1,2,Guangxiang HE1,2,Suohe YANG1,2,Xiaoyan GUO1,2,Rongyue ZHANG1,2
Received:2021-01-29
Revised:2021-05-31
Online:2021-09-05
Published:2021-09-05
Contact:
Haibo JIN
摘要:
计算流体力学与群体平衡模型(CFD-PBM)结合可有效地模拟鼓泡塔内流体行为,较准确地预测流场、相含率以及局部气泡尺寸分布。以直径100 mm、高1.3 m的加温加压鼓泡塔为模拟对象,在系统压力为1 MPa、表观气速为0.08~0.24 m/s、温度为30~160℃条件下系统地考察了空气-水体系的表观气速、温度以及固含率对平均气含率、大小气泡气含率、气泡直径和气泡尺寸分布等参数的影响。结果表明,平均气含率的模拟结果和实验值在10%的误差范围内吻合较好;温度的变化主要影响了塔内气泡的聚并和破碎,并用聚并破碎的机理解释了温度对其流体行为的影响。
中图分类号:
张文龙, 侯燕, 靳海波, 马磊, 何广湘, 杨索和, 郭晓燕, 张荣月. 加温加压下CFD-PBM耦合模型空气-水两相流数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4594-4606.
Wenlong ZHANG, Yan HOU, Haibo JIN, Lei MA, Guangxiang HE, Suohe YANG, Xiaoyan GUO, Rongyue ZHANG. Numerical simulation of air-water two-phase flow under elevated pressures and temperatures using CFD-PBM coupled model[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4594-4606.
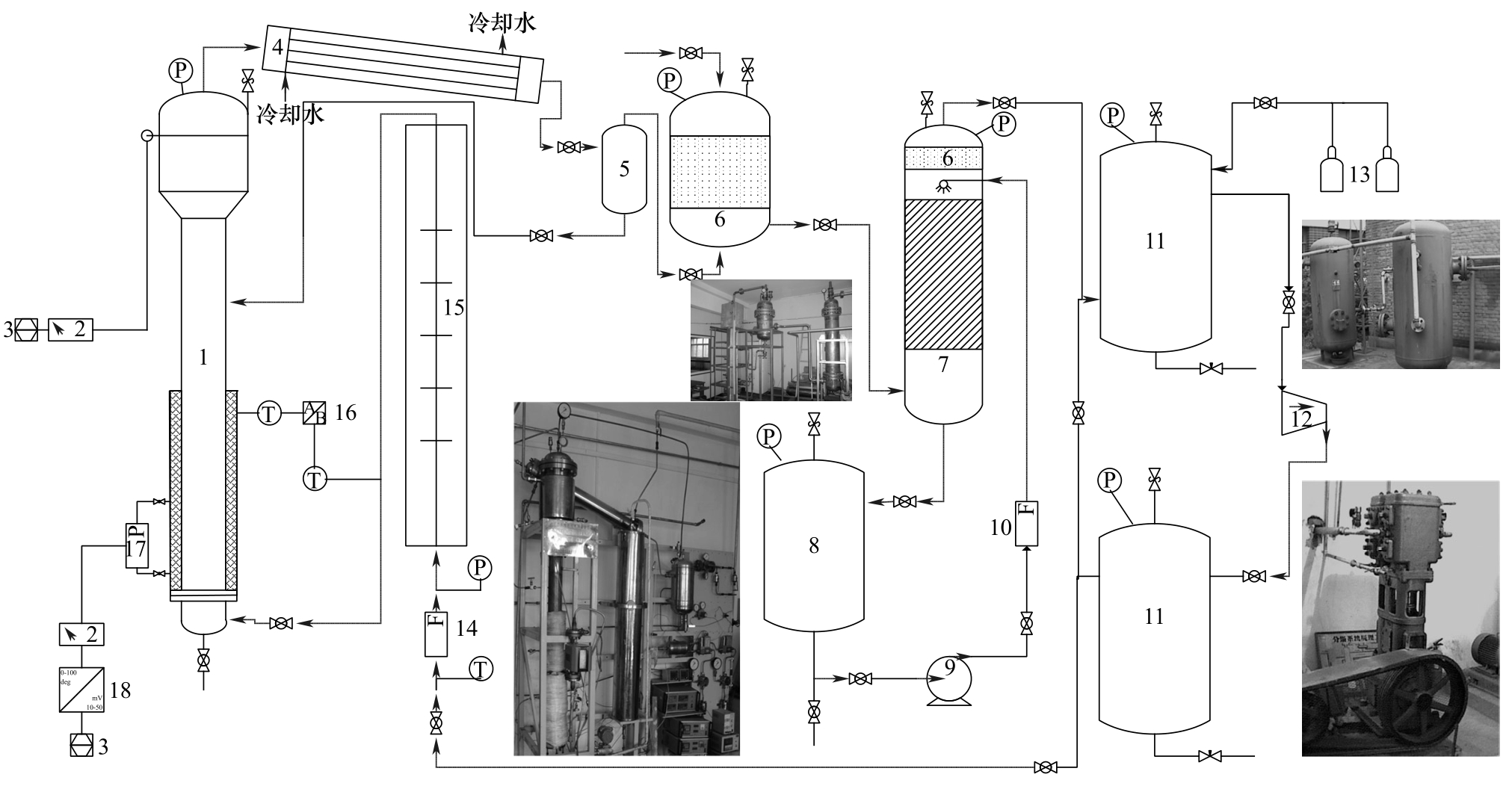
图1 实验装置流程图1—鼓泡塔;2—指示器;3—计算机;4—冷却器;5—气液分离器;6—丝网除沫器;7—填料吸收塔;8—碱液储罐;9—离心泵;10—流量计;11—储罐;12—压缩机;13—N2钢瓶;14—转子流量计;15—气体预热器;16—温控仪;17—差压传感器;18—A/D转换器
Fig.1 Experimental device
| 气液相 | 黏度/ (mPa·s) | 密度/ (kg/m3) | 表面张力/ (mN/m) | 固含率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O Ⅰ 35℃ | 0.7340 | 992.6 | 69.83 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅰ 100℃ | 0.2820 | 990.1 | 58.84 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅰ 160℃ | 0.1740 | 993.9 | 46.58 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅱ 45℃ | 0.8264 | 1017.5 | 68.65 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅱ 100℃ | 0.2915 | 985.4 | 58.84 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅱ 160℃ | 0.1792 | 934.8 | 46.58 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅲ 60℃ | 0.5225 | 1064.0 | 66.20 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅲ 100℃ | 0.3139 | 1039.0 | 58.84 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅲ 160℃ | 0.1930 | 1016.0 | 46.58 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅳ 30℃ | 0.9780 | 1130.9 | 70.42 | 25 |
| H2O Ⅳ 100℃ | 0.3449 | 1095.4 | 58.84 | 25 |
| H2O Ⅳ 160℃ | 0.2120 | 1044.4 | 46.58 | 25 |
| 空气(1 MPa) | 0.0179 | 12.09 |
表1 气液物性
Table 1 Physical properties of gas and liquid
| 气液相 | 黏度/ (mPa·s) | 密度/ (kg/m3) | 表面张力/ (mN/m) | 固含率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O Ⅰ 35℃ | 0.7340 | 992.6 | 69.83 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅰ 100℃ | 0.2820 | 990.1 | 58.84 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅰ 160℃ | 0.1740 | 993.9 | 46.58 | 0 |
| H2O Ⅱ 45℃ | 0.8264 | 1017.5 | 68.65 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅱ 100℃ | 0.2915 | 985.4 | 58.84 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅱ 160℃ | 0.1792 | 934.8 | 46.58 | 5 |
| H2O Ⅲ 60℃ | 0.5225 | 1064.0 | 66.20 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅲ 100℃ | 0.3139 | 1039.0 | 58.84 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅲ 160℃ | 0.1930 | 1016.0 | 46.58 | 15 |
| H2O Ⅳ 30℃ | 0.9780 | 1130.9 | 70.42 | 25 |
| H2O Ⅳ 100℃ | 0.3449 | 1095.4 | 58.84 | 25 |
| H2O Ⅳ 160℃ | 0.2120 | 1044.4 | 46.58 | 25 |
| 空气(1 MPa) | 0.0179 | 12.09 |
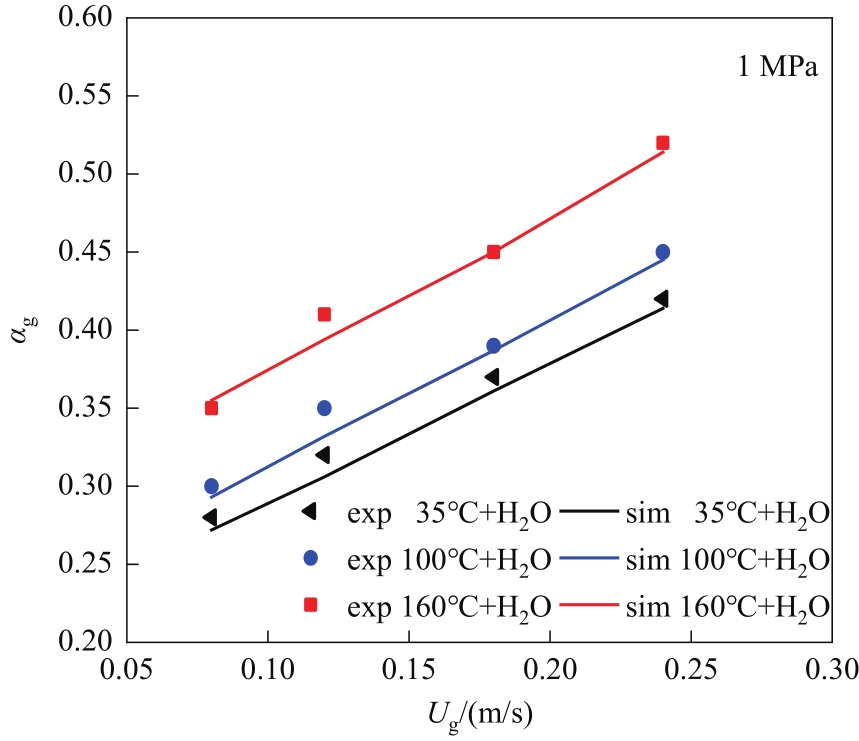
图4 不同温度下空气-水体系表观气速与平均气含率的关系
Fig.4 The relationship between superficial gas velocity of air-water system and average gas holdup under different temperatures

图7 不同温度下空气-水体系温度与大小气泡气含率的关系
Fig.7 The relationship between temperature of the air-water system and large and small bubbles gas holdup under different temperatures

图13 不同温度下空气-水体系温度与气泡数密度分布的关系
Fig.13 The relationship between temperature of air-water system and bubble number density distribution under different temperatures
| 1 | Shi W B, Yang J, Li G, et al. Modelling of breakage rate and bubble size distribution in bubble columns accounting for bubble shape variations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 187: 391-405. |
| 2 | Yan P, Jin H B, Gao X, et al. Numerical analysis of bubble characteristics in a pressurized bubble column using CFD coupled with a population balance model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 234: 116427. |
| 3 | Zhang B, Kong L T, Jin H B, et al. CFD simulation of gas-liquid flow in a high-pressure bubble column with a modified population balance model[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 26(6): 1350-1358. |
| 4 | Tao F F, Ning S L, Zhang B, et al. Simulation study on gas holdup of large and small bubbles in a high pressure gas-liquid bubble column[J]. Processes, 2019, 7(9): 594. |
| 5 | Deckwer W D, Louisi Y, Zaidi A, et al. Hydrodynamic properties of the Fischer-Tropsch slurry process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1980, 19(4): 699-708. |
| 6 | Behkish A, Lemoine R, Sehabiague L, et al. Gas holdup and bubble size behavior in a large-scale slurry bubble column reactor operating with an organic liquid under elevated pressures and temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 128(2/3): 69-84. |
| 7 | Pohorecki R, Moniuk W, Zdrójkowski A, et al. Hydrodynamics of a pilot plant bubble column under elevated temperature and pressure[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(3): 1167-1174. |
| 8 | Zhang H H, Sayyar A, Wang Y L, et al. Generality of the CFD-PBM coupled model for bubble column simulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 219: 115514. |
| 9 | 徐琰, 董海峰, 田肖, 等. 鼓泡塔中离子液体-空气两相流的CFD-PBM耦合模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(10): 2699-2706. |
| Xu Y, Dong H F, Tian X, et al. CFD-PBM coupled simulation of ionic liquid-air two-phase flow in bubble column[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(10): 2699-2706. | |
| 10 | 王珏, 杨宁. 基于EMMS方法的鼓泡塔反应器CFD及群平衡模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(7): 2667-2677. |
| Wang J, Yang N. CFD-PBM simulation with EMMS correctors for bubble column reactors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(7): 2667-2677. | |
| 11 | Yan P, Jin H B, He G X, et al. CFD simulation of hydrodynamics in a high-pressure bubble column using three optimized drag models of bubble swarm[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 199: 137-155. |
| 12 | van Baten J M, Krishna R. CFD simulations of a bubble column operating in the homogeneous and heterogeneous flow regimes[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2002, 25(11): 1081-1086. |
| 13 | Scargiali F, D'Orazio A, Grisafi F, et al. Modelling and simulation of gas-liquid hydrodynamics in mechanically stirred tanks[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2007, 85(5): 637-646. |
| 14 | Buffo A, Vanni M, Renze P, et al. Empirical drag closure for polydisperse gas-liquid systems in bubbly flow regime: bubble swarm and micro-scale turbulence[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2016, 113: 284-303. |
| 15 | Roghair I, van Sint Annaland M, Kuipers H J A M. Drag force and clustering in bubble swarms[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(5): 1791-1800. |
| 16 | Wang T F, Wang J F, Jin Y. A CFD-PBM coupled model for gas-liquid flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 2006, 52(1): 125-140. |
| 17 | Tomiyama A. Struggle with computational bubble dynamics[J]. Multiphase Science and Technology, 1998, 10(4): 369-405. |
| 18 | Yang N, Chen J H, Zhao H, et al. Explorations on the multi-scale flow structure and stability condition in bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(24): 6978-6991. |
| 19 | Yang N, Wu Z Y, Chen J H, et al. Multi-scale analysis of gas-liquid interaction and CFD simulation of gas-liquid flow in bubble columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(14): 3212-3222. |
| 20 | Qin C P, Chen C, Xiao Q, et al. CFD-PBM simulation of droplets size distribution in rotor-stator mixing devices[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 16-26. |
| 21 | Yang N, Xiao Q. A mesoscale approach for population balance modeling of bubble size distribution in bubble column reactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 170: 241-250. |
| 22 | Tabib M V, Roy S A, Joshi J B. CFD simulation of bubble column—an analysis of interphase forces and turbulence models[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 139(3): 589-614. |
| 23 | 张煜. 湍动鼓泡塔充分发展段的流体力学与内构件技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011. |
| Zhang Y. Hydrodynamics of turbulent bubble column with internals in well-developed flow region[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011. | |
| 24 | Frank T, Zwart P J, Krepper E, et al. Validation of CFD models for mono- and polydisperse air-water two-phase flows in pipes[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008, 238(3): 647-659. |
| 25 | Lopez de Bertodano M, Lahey R T, Jones O C. Turbulent bubbly two-phase flow data in a triangular duct[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1994, 146(1/2/3): 43-52. |
| 26 | Luo H, Svendsen H F. Theoretical model for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions[J]. AIChE Journal, 1996, 42(5): 1225-1233. |
| 27 | Lehr F, Millies M, Mewes D. Bubble-size distributions and flow fields in bubble columns[J]. AIChE Journal, 2002, 48(11): 2426-2443. |
| 28 | Luo H, Svendsen H F. Modeling and simulation of binary approach by energy conservation analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1996, 145(1): 145-153. |
| 29 | 黄娟, 戴干策. 升温鼓泡塔内有机溶液的气含率[J]. 过程工程学报, 2008, 8(2): 209-216. |
| Huang J, Dai G C. Gas holdup in a bubble column at elevated temperature with organic liquid solutions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2008, 8(2): 209-216. | |
| 30 | Behkish A, Lemoine R, Oukaci R, et al. Novel correlations for gas holdup in large-scale slurry bubble column reactors operating under elevated pressures and temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 115(3): 157-171. |
| 31 | Ishii M, Zuber N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 1979, 25(5): 843-855. |
| 32 | Chabot J, de Lasa H I. Gas holdups and bubble characteristics in a bubble column operated at high temperature[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1993, 32(11): 2595-2601. |
| 33 | 李兆奇. 列管型鼓泡塔中流动发展规律的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015. |
| Li Z Q. Flow development in bubble columns with pipe bundle internals[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. |
| [1] | 周绍华, 詹飞龙, 丁国良, 张浩, 邵艳坡, 刘艳涛, 郜哲明. 短管节流阀内流动噪声的实验研究及降噪措施[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 113-121. |
| [2] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [3] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [4] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [5] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [6] | 王玉兵, 李杰, 詹宏波, 朱光亚, 张大林. R134a在菱形离散肋微小通道内的流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [7] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [8] | 袁佳琦, 刘政, 黄锐, 张乐福, 贺登辉. 泡状入流条件下旋流泵能量转换特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3807-3820. |
| [9] | 岳林静, 廖艺涵, 薛源, 李雪洁, 李玉星, 刘翠伟. 凹坑缺陷对厚孔板喉部空化流动特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3292-3308. |
| [10] | 高燕, 伍鹏, 尚超, 胡泽君, 陈晓东. 基于双流体喷嘴的磁性琼脂糖微球的制备及其蛋白吸附性能探究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [11] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [12] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [13] | 郭雨莹, 敬加强, 黄婉妮, 张平, 孙杰, 朱宇, 冯君炫, 陆洪江. 稠油管道水润滑减阻及压降预测模型修正[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2898-2907. |
| [14] | 高金明, 郭玉娇, 鄂承林, 卢春喜. 一种封闭罩内顺流多旋臂气液分离器的分离特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2957-2966. |
| [15] | 何宣志, 何永清, 闻桂叶, 焦凤. 磁液液滴颈部自相似破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号