化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (5): 1930-1939.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211767
殷亚然1( ),朱星星1,张先明1,朱春英2,付涛涛2,马友光2(
),朱星星1,张先明1,朱春英2,付涛涛2,马友光2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-14
修回日期:2022-03-02
出版日期:2022-05-05
发布日期:2022-05-24
通讯作者:
马友光
作者简介:殷亚然(1990—),女,博士,讲师,基金资助:
Yaran YIN1( ),Xingxing ZHU1,Xianming ZHANG1,Chunying ZHU2,Taotao FU2,Youguang MA2(
),Xingxing ZHU1,Xianming ZHANG1,Chunying ZHU2,Taotao FU2,Youguang MA2( )
)
Received:2021-12-14
Revised:2022-03-02
Online:2022-05-05
Published:2022-05-24
Contact:
Youguang MA
摘要:
研究了微通道内醇胺[单乙醇胺(MEA)和甲基二乙醇胺(MDEA)]与离子液体[1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑四氟硼酸([Bmim][BF4])和1-羟乙基-3-甲基咪唑甘氨酸([C2OHmim][GLY])]复配水溶液吸收CO2的传质特性。考察了醇胺/离子液体浓度比(cAA∶cIL)对液相体积传质系数(kLa)的影响,发现kLa随反应速率的增大而增大。为进一步阐释复配水溶液吸收CO2的传质机理,分析了比表面积、扩散速率、增强因子和液弹循环对传质速率的影响。结果表明,四种复配溶液中,反应速率和循环频率(fcir)分别在低流率和高流率下对传质速率起主导作用。kLa可表示为fcir的函数,低气相流率下kLa与fcir呈线性关系,斜率与反应速率成正相关,高气相流率下,液弹循环因膜弹传递困难而对整体传质速率的影响减弱,kLa与fcir呈指数关系,幂律指数小于1。
中图分类号:
殷亚然, 朱星星, 张先明, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 马友光. 微通道内醇胺/离子液体复配水溶液吸收CO2的传质特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 1930-1939.
Yaran YIN, Xingxing ZHU, Xianming ZHANG, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Youguang MA. Mass transfer characteristics of CO2 absorption in alkanolamine/ionic liquid hybrid aqueous solutions in a microchannel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 1930-1939.
| 溶液 | cAA∶cIL | 密度ρL/(g/cm3) | 黏度ηL/(mPa·s) | 表面张力σ/(mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEA/[Bmim][BF4] | 5∶5 | 1.0169 | 1.000 | 37.84 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0135 | 0.983 | 37.73 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0100 | 0.962 | 37.40 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0064 | 0.950 | 37.16 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0029 | 0.934 | 36.82 | |
| 10∶0 | 0.9993 | 0.952 | 39.77 | |
| MEA/[C2OHmim][GLY] | 5∶5 | 1.0214 | 1.078 | 37.39 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0170 | 1.041 | 37.90 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0125 | 1.008 | 38.45 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0082 | 0.964 | 38.95 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0037 | 0.930 | 39.45 | |
| MDEA/[Bmim][BF4] | 5∶5 | 1.0187 | 1.045 | 35.76 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0182 | 1.083 | 35.74 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0155 | 1.105 | 35.71 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0129 | 1.114 | 35.68 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0101 | 1.141 | 35.63 | |
| 10∶0 | 1.0066 | 1.155 | 38.52 | |
| MDEA/[C2OHmim][GLY] | 5∶5 | 1.0254 | 1.216 | 37.95 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0217 | 1.215 | 38.36 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0185 | 1.213 | 39.15 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0146 | 1.208 | 39.65 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0110 | 1.201 | 40.44 |
表1 醇胺/离子液体复配水溶液的物理性质
Table 1 Physical properties of various alkanolamine/ionic liquid aqueous solutions
| 溶液 | cAA∶cIL | 密度ρL/(g/cm3) | 黏度ηL/(mPa·s) | 表面张力σ/(mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEA/[Bmim][BF4] | 5∶5 | 1.0169 | 1.000 | 37.84 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0135 | 0.983 | 37.73 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0100 | 0.962 | 37.40 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0064 | 0.950 | 37.16 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0029 | 0.934 | 36.82 | |
| 10∶0 | 0.9993 | 0.952 | 39.77 | |
| MEA/[C2OHmim][GLY] | 5∶5 | 1.0214 | 1.078 | 37.39 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0170 | 1.041 | 37.90 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0125 | 1.008 | 38.45 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0082 | 0.964 | 38.95 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0037 | 0.930 | 39.45 | |
| MDEA/[Bmim][BF4] | 5∶5 | 1.0187 | 1.045 | 35.76 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0182 | 1.083 | 35.74 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0155 | 1.105 | 35.71 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0129 | 1.114 | 35.68 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0101 | 1.141 | 35.63 | |
| 10∶0 | 1.0066 | 1.155 | 38.52 | |
| MDEA/[C2OHmim][GLY] | 5∶5 | 1.0254 | 1.216 | 37.95 |
| 6∶4 | 1.0217 | 1.215 | 38.36 | |
| 7∶3 | 1.0185 | 1.213 | 39.15 | |
| 8∶2 | 1.0146 | 1.208 | 39.65 | |
| 9∶1 | 1.0110 | 1.201 | 40.44 |
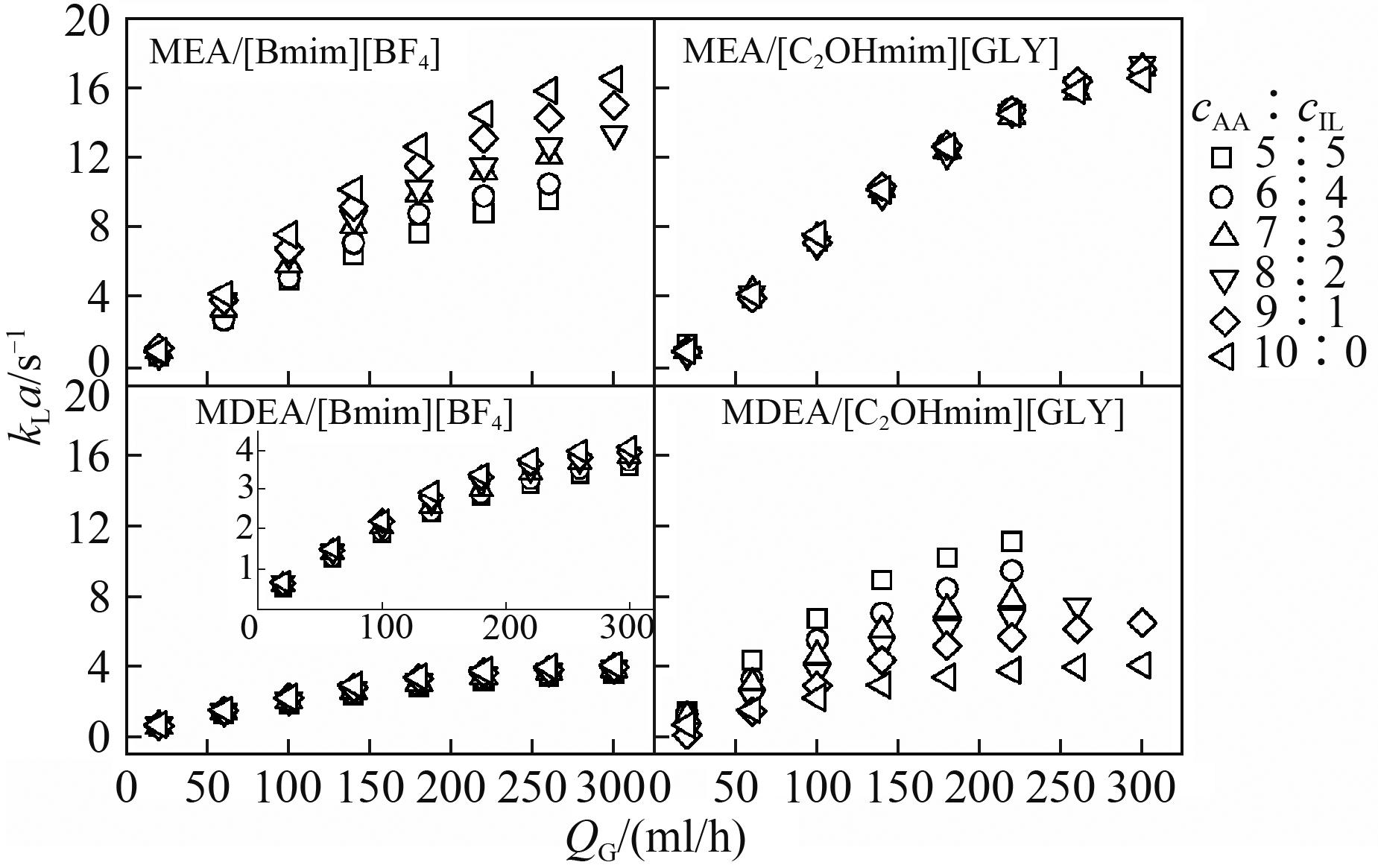
图4 液相浓度比对液相体积传质系数(kLa)的影响
Fig.4 Effects of concentration ratio of alkanolamine to ionic liquid on the liquid-phase volumetric mass transfer coefficient (kLa)
| cAA∶cIL | MEA/ [Bmim][BF4] | MEA/ [C2OHmim][GLY] | MDEA/[Bmim][BF4] | MDEA/ [C2OHmim][GLY] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | α | β | α | β | α | β | |
| 5∶5 | 0.029 | 3.692 | 0.057 | 5.320 | 0.019 | 1.140 | 0.041 | 4.336 |
| 6∶4 | 0.034 | 3.740 | 0.059 | 5.111 | 0.017 | 1.692 | 0.041 | 3.561 |
| 7∶3 | 0.043 | 3.776 | 0.063 | 4.677 | 0.019 | 1.662 | 0.033 | 3.519 |
| 8∶2 | 0.047 | 3.636 | 0.058 | 4.917 | 0.022 | 1.306 | 0.031 | 3.067 |
| 9∶1 | 0.050 | 4.191 | 0.060 | 4.962 | 0.023 | 1.256 | 0.027 | 2.582 |
| 10∶0 | 0.059 | 4.292 | 0.059 | 4.292 | 0.022 | 1.459 | 0.020 | 1.693 |
表2 不同复配溶液的拟合系数α和β
Table 2 Coefficients α and β for different alkanolamine/ionic liquid solutions
| cAA∶cIL | MEA/ [Bmim][BF4] | MEA/ [C2OHmim][GLY] | MDEA/[Bmim][BF4] | MDEA/ [C2OHmim][GLY] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | α | β | α | β | α | β | |
| 5∶5 | 0.029 | 3.692 | 0.057 | 5.320 | 0.019 | 1.140 | 0.041 | 4.336 |
| 6∶4 | 0.034 | 3.740 | 0.059 | 5.111 | 0.017 | 1.692 | 0.041 | 3.561 |
| 7∶3 | 0.043 | 3.776 | 0.063 | 4.677 | 0.019 | 1.662 | 0.033 | 3.519 |
| 8∶2 | 0.047 | 3.636 | 0.058 | 4.917 | 0.022 | 1.306 | 0.031 | 3.067 |
| 9∶1 | 0.050 | 4.191 | 0.060 | 4.962 | 0.023 | 1.256 | 0.027 | 2.582 |
| 10∶0 | 0.059 | 4.292 | 0.059 | 4.292 | 0.022 | 1.459 | 0.020 | 1.693 |
| 1 | Yu C H, Huang C H, Tan C S. A review of CO2 capture by absorption and adsorption[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2012, 12(5): 745-769. |
| 2 | 林海周, 裴爱国, 方梦祥. 燃煤电厂烟气二氧化碳胺法捕集工艺改进研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(12): 4874-4886. |
| Lin H Z, Pei A G, Fang M X. Progress of research on process modifications for amine solvent-based post combustion CO2 capture from coal-fired power plant[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(12): 4874-4886. | |
| 3 | 张卫风, 许元龙, 王秋华. CO2醇胺富液低能耗再生研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(8): 4497-4507. |
| Zhang W F, Xu Y L, Wang Q H. Progress of research on regeneration of rich alkanolamine solution with low energy consumption[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(8): 4497-4507. | |
| 4 | Veawab A, Tontiwachwuthikul P, Chakma A. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in the CO2 absorption process using aqueous amine solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(10): 3917-3924. |
| 5 | MacDowell N, Florin N, Buchard A, et al. An overview of CO2 capture technologies[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(11): 1645. |
| 6 | Bates E D, Mayton R D, Ntai I, et al. CO2 capture by a task-specific ionic liquid[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(6): 926-927. |
| 7 | Zhang Y Y, Ji X Y, Xie Y J, et al. Screening of conventional ionic liquids for carbon dioxide capture and separation[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1160-1170. |
| 8 | Liao H Y, Gao H X, Xu B, et al. Mass transfer performance studies of aqueous blended DEEA-MEA solution using orthogonal array design in a packed column[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 183: 117-126. |
| 9 | 李孟盈, 吕春捷, 徐立华, 等. 离子液体-醇胺水溶液捕集CO2研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(2): 70-74. |
| Li M Y, Lyu C J, Xu L H, et al. Research progress in CO2 capture by ionic liquids-alkanolamine aqueous solutions[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(2): 70-74. | |
| 10 | 夏裴文, 王强, 张鹏军, 等. 氨基酸离子液体-MDEA复配液对CO2的吸收[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2019, 35(2): 123-130. |
| Xia P W, Wang Q, Zhang P J, et al. Absorptin of CO2 by amino acid ionic liquid-MDEA complex solution[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption. 2019, 35(2): 123-130. | |
| 11 | Ahmady A, Hashim M A, Aroua M K. Kinetics of carbon dioxide absorption into aqueous MDEA +[bmim][BF 4] solutions from 303 to 333 K[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 200/201/202: 317-328. |
| 12 | Lu B H, Wang X Q, Xia Y F, et al. Kinetics of carbon dioxide absorption into mixed aqueous solutions of MEA + [Bmim][BF4] using a double stirred cell[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(10): 6002-6009. |
| 13 | Lu B H, Jin J J, Zhang L, et al. Absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous blend of monoethanolamine and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 11: 152-157. |
| 14 | Lv B H, Shi Y, Sun C, et al. CO2 capture by a highly-efficient aqueous blend of monoethanolamine and a hydrophilic amino acid ionic liquid[C2OHmim][Gly][J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 372-377. |
| 15 | Lv B H, Sun C, Liu N, et al. Mass transfer and kinetics of CO2 absorption into aqueous monoethanolamine/1-hydroxyethy-3-methyl imidazolium glycinate solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 280: 695-702. |
| 16 | Exposito A J, Bai Y, Tchabanenko K, et al. Process intensification of continuous-flow imine hydrogenation in catalyst-coated tube reactors[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(11): 4433-4442. |
| 17 | Sansotera M, Baggioli A, Ieffa S, et al. Catalytic microreactor with electrodeposited hierarchically nanostructured nickel coatings for gas-phase fluorination reactions[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2018, 205: 22-29. |
| 18 | Liu S E, Li G X, Shang M J, et al. Hydrodynamics study of a fast liquid-liquid oxidation process with in situ gas production in microreactors[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(11): e17362. |
| 19 | 丁云成, 王法军, 艾宁, 等. 微反应器内连续重氮化/偶合反应进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(11): 4542-4552. |
| Ding Y C, Wang F J, Ai N, et al. Research progress on continuous diazotization/azo-coupling reaction in microreactors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(11): 4542-4552. | |
| 20 | Yao C Q, Zhu K, Liu Y Y, et al. Intensified CO2 absorption in a microchannel reactor under elevated pressures[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 319: 179-190. |
| 21 | 尧超群, 乐军, 赵玉潮, 等. 微通道内气-液弹状流动及传质特性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(8): 2759-2766. |
| Yao C Q, Yue J, Zhao Y C, et al. Review on flow and mass transfer characteristics of gas-liquid slug flow in microchannels[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(8): 2759-2766. | |
| 22 | Berčič G, Pintar A. The role of gas bubbles and liquid slug lengths on mass transport in the Taylor flow through capillaries[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(21/22): 3709-3719. |
| 23 | van Baten J M, Krishna R. CFD simulations of mass transfer from Taylor bubbles rising in circular capillaries[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2004, 59(12): 2535-2545. |
| 24 | Sobieszuk P, Pohorecki R, Cygański P, et al. Determination of the interfacial area and mass transfer coefficients in the Taylor gas-liquid flow in a microchannel[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(23): 6048-6056. |
| 25 | Zhang P, Yao C Q, Ma H Y, et al. Dynamic changes in gas-liquid mass transfer during Taylor flow in long serpentine square microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 182: 17-27. |
| 26 | Yao C Q, Zhao Y C, Zheng J, et al. The effect of liquid viscosity and modeling of mass transfer in gas-liquid slug flow in a rectangular microchannel[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(5): e16934. |
| 27 | Butler C, Lalanne B, Sandmann K, et al. Mass transfer in Taylor flow: transfer rate modelling from measurements at the slug and film scale[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2018, 105: 185-201. |
| 28 | Butler C, Cid E, Billet A M. Modelling of mass transfer in Taylor flow: investigation with the PLIF-I technique[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2016, 115: 292-302. |
| 29 | Abiev R S, Butler C, Cid E, et al. Mass transfer characteristics and concentration field evolution for gas-liquid Taylor flow in milli channels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 1331-1340. |
| 30 | 张筱丽, MDEA/氨基酸功能性离子液体混合水溶液吸收CO 2 的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. |
| Zhang X L. CO2 absorption into the mixed aqueous solution of MDEA and amino acid ionic liquid[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016. | |
| 31 | Last W, Stichlmair J. Determination of mass transfer parameters by means of chemical absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2002, 25(4): 385-391. |
| 32 | Kockmann N, Karlen S, Girard C, et al. Liquid-liquid test reactions to characterize two-phase mixing in microchannels[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2013, 34(2/3): 169-177. |
| 33 | Shao N, Gavriilidis A, Angeli P. Mass transfer during Taylor flow in microchannels with and without chemical reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 160(3): 873-881. |
| 34 | 姜山, 朱春英, 张璠玢, 等. 微通道内单乙醇胺水溶液吸收CO2/N2混合气的传质特性[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(2): 643-652. |
| Jiang S, Zhu C Y, Zhang F B, et al. Mass transfer performance of CO2/N2 mixture absorption into monoethanolamine aqueous solution in microchannel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(2): 643-652. | |
| 35 | Ganapathy H, Steinmayer S, Shooshtari A, et al. Process intensification characteristics of a microreactor absorber for enhanced CO2 capture[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 416-427. |
| 36 | Yao C Q, Dong Z Y, Zhao Y C, et al. An online method to measure mass transfer of slug flow in a microchannel[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 112: 15-24. |
| 37 | Garstecki P, Fuerstman M J, Stone H A, et al. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction-scaling and mechanism of break-up[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6(3): 437-446. |
| 38 | Guo R W, Fu T T, Zhu C Y, et al. Pressure drop model of gas-liquid flow with mass transfer in tree-typed microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125340. |
| 39 | Yue J, Luo L G, Gonthier Y, et al. An experimental study of air-water Taylor flow and mass transfer inside square microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(16): 3697-3708. |
| 40 | Aussillous P, Quéré D. Quick deposition of a fluid on the wall of a tube[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2000, 12(10): 2367-2371. |
| 41 | Yao C Q, Zheng J, Zhao Y C, et al. Characteristics of gas-liquid Taylor flow with different liquid viscosities in a rectangular microchannel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 373: 437-445. |
| 42 | Ganapathy H, Shooshtari A, Dessiatoun S, et al. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer performance of a microreactor for enhanced gas separation processes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 266: 258-270. |
| 43 | Saha A K, Bandyopadhyay S S, Biswas A K. Solubility and diffusivity of nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide in aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 1993, 38: 78-82. |
| 44 | Tan J, Lu Y C, Xu J H, et al. Mass transfer characteristic in the formation stage of gas-liquid segmented flow in microchannel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 185/186: 314-320. |
| 45 | Zheng C, Zhao B C, Wang K, et al. Determination of kinetics of CO2 absorption in solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol using a microfluidic technique[J]. AIChE Journal, 2015, 61(12): 4358-4366. |
| 46 | Ganapathy H, Shooshtari A, Dessiatoun S, et al. Fluid flow and mass transfer characteristics of enhanced CO2 capture in a minichannel reactor[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 119: 43-56. |
| 47 | Mei M, Hébrard G, Dietrich N, et al. Gas-liquid mass transfer around Taylor bubbles flowing in a long, in-plane, spiral-shaped milli-reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 222: 115717. |
| 48 | Abiev R S. Bubbles velocity, Taylor circulation rate and mass transfer model for slug flow in milli- and microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 227: 66-79. |
| 49 | Abiev R S. Circulation and bypass modes of the slug flow of a gas-liquid mixture in capillaries[J]. Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 43(3): 298-306. |
| 50 | Sun R P, Cubaud T. Dissolution of carbon dioxide bubbles and microfluidic multiphase flows[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2011, 11(17): 2924-2928. |
| 51 | Yin Y R, Fu T T, Zhu C Y, et al. Dynamics and mass transfer characteristics of CO2 absorption into MEA/[Bmim][BF4] aqueous solutions in a microchannel[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 210: 541-552. |
| 52 | Ma D F, Zhu C Y, Fu T T, et al. An effective hybrid solvent of MEA/DEEA for CO2 absorption and its mass transfer performance in microreactor[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 242: 116795. |
| [1] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [2] | 王琪, 张斌, 张晓昕, 武虎建, 战海涛, 王涛. 氯铝酸-三乙胺离子液体/P2O5催化合成伊索克酸和2-乙基蒽醌[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [3] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [4] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [5] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [6] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [7] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [8] | 王俐智, 杭钱程, 郑叶玲, 丁延, 陈家继, 叶青, 李进龙. 离子液体萃取剂萃取精馏分离丙酸甲酯+甲醇共沸物[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741. |
| [9] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [10] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [11] | 宋明昊, 赵霏, 刘淑晴, 李国选, 杨声, 雷志刚. 离子液体脱除模拟油中挥发酚的多尺度模拟与研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [12] | 袁佳琦, 刘政, 黄锐, 张乐福, 贺登辉. 泡状入流条件下旋流泵能量转换特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3807-3820. |
| [13] | 杨绍旗, 赵淑蘅, 陈伦刚, 王晨光, 胡建军, 周清, 马隆龙. Raney镍-质子型离子液体体系催化木质素平台分子加氢脱氧制备烷烃[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [14] | 陆俊凤, 孙怀宇, 王艳磊, 何宏艳. 离子液体界面极化及其调控氢键性质的分子机理[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3665-3680. |
| [15] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号